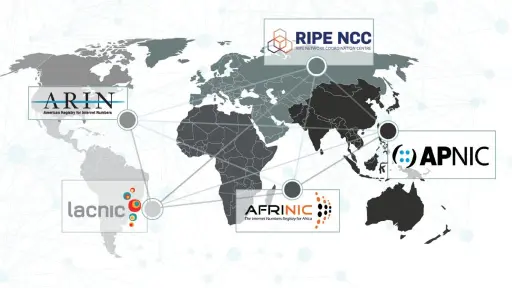
- Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) allocate and manage IP addresses and Autonomous System numbers across distinct global regions.
- There are five RIRs, each responsible for a specific geographic area, ensuring fair distribution of internet resources.
- RIRs face challenges like IPv4 exhaustion and advocate for IPv6 adoption to meet growing internet connectivity demands.
In today’s digital age, the management of internet resources, such as IP addresses and Autonomous System (AS) numbers, is crucial for the seamless operation of the global network. At the forefront of this management are entities known as Regional Internet Registries (RIRs).
A Regional Internet Registry (RIR) is an organization responsible for allocating and managing IP addresses and related resources within a specific region of the world. The primary goal of an RIR is to ensure fair and efficient distribution of these resources, which are vital for the operation of the internet.
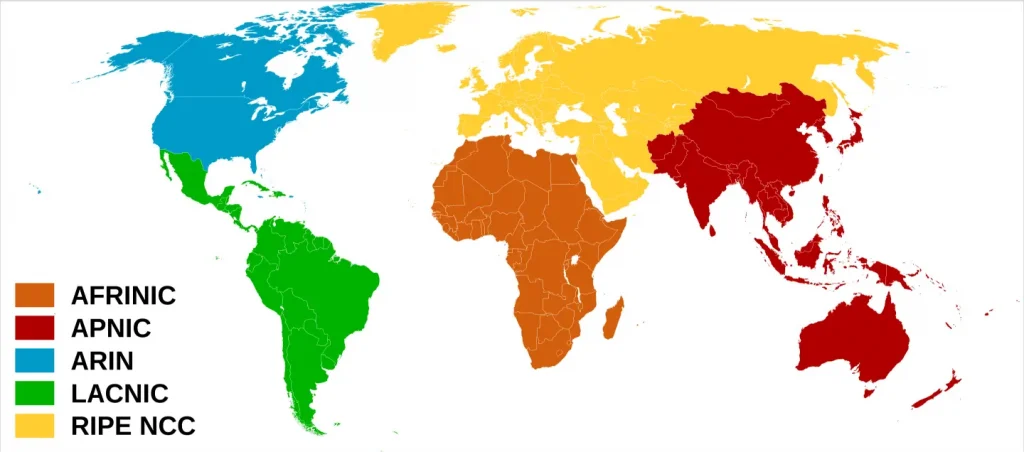
The global structure of RIRs
There are five RIRs globally, each overseeing a distinct geographic area:
1. American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN) – Covers North America.
2. Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC) – Manages Europe, the Middle East, and parts of Central Asia.
3. Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC) – Responsible for Asia and the Pacific region.
4. Latin American and Caribbean Internet Addresses Registry (LACNIC) – Oversees Latin America and the Caribbean.
5. African Network Information Centre (AFRINIC) – Manages IP resources in Africa.
Also read: Randy Bush honoured at RIPE 87 after calling RIRs a ‘monopoly’
Functions of RIRs
– Allocation and Management of IP Addresses: RIRs allocate IP address blocks to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), large organizations, and sometimes to end users. They manage both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
– Autonomous System Numbers Management: RIRs assign AS numbers used for routing internet traffic.
– Policy Development: RIRs develop policies regarding the allocation and management of internet resources. These policies are created through a community-driven process, ensuring transparency and representation of various stakeholders.
– Technical Services: They provide services such as reverse DNS delegations and maintain WHOIS databases for their regions, offering information about IP address allocations.
– Education and Outreach: RIRs conduct training and workshops to educate stakeholders about internet resources management and best practices.
Also read: ICANN’s Africa DNS report barely mentions the AFRINIC problem
Importance in the internet ecosystem
RIRs play a critical role in the global internet ecosystem. They ensure that IP resources are used efficiently and are available for future needs. By facilitating fair and stable distribution, RIRs contribute to the resilience and growth of the internet.
Challenges and future outlook
With the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, RIRs are actively encouraging the adoption of IPv6 to meet the growing demand for internet connectivity. They also face challenges like ensuring equitable access to resources across diverse regions and addressing issues related to internet governance.In conclusion, Regional Internet Registries are pivotal in managing key internet resources, maintaining operational stability, and shaping the future of global internet connectivity.