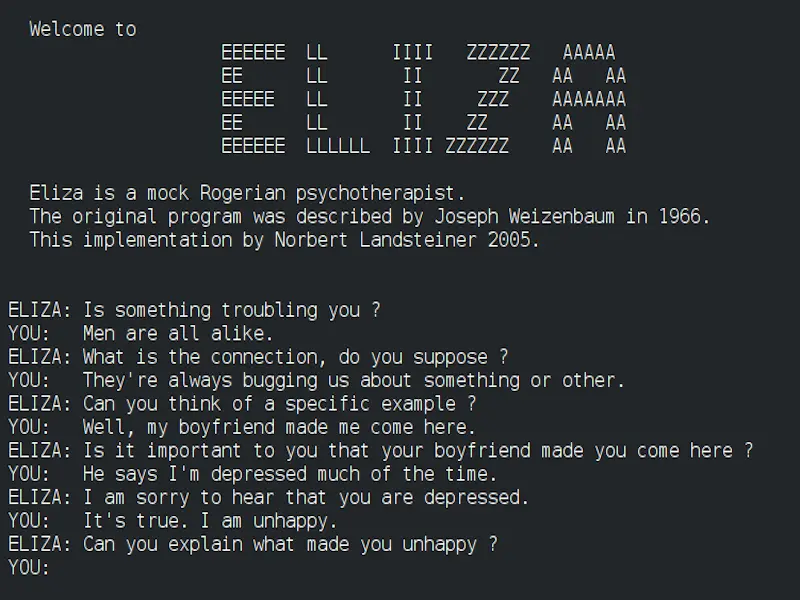
- The first virtual assistant can be traced back to 1966, when Joseph Weizenbaum, a computer scientist at MIT, created ELIZA.
- Although limited in its capabilities, ELIZA paved the way for the development of more advanced virtual assistants.
The birth of ELIZA: A groundbreaking AI milestone
In 1966, Joseph Weizenbaum, a computer scientist at MIT, introduced ELIZA, a revolutionary program that marked a significant milestone in the field of artificial intelligence. ELIZA was designed to simulate human conversation, drawing inspiration from the psychotherapy methods of the time. Weizenbaum aimed to create a digital counterpart to a Rogerian psychotherapist, known for its technique of reflective listening.
ELIZA operated using a relatively simple pattern-matching algorithm, which allowed it to identify and respond to specific keywords and phrases in user input. For instance, if a user expressed feeling “sad,” ELIZA might respond with a reflective question like, “Why do you feel sad?” Despite its basic design, the program managed to create the illusion of understanding and intelligent conversation. This was achieved by cleverly manipulating the input data to produce contextually appropriate responses.
Although ELIZA’s technology was primitive compared to today’s standards, its impact was profound. The program demonstrated that machines could engage in seemingly intelligent dialogues, sparking interest and further exploration in AI research. ELIZA’s success was not merely a technical achievement; it also challenged prevailing notions about the nature of intelligence and the capabilities of machines. By creating a convincing conversational experience, ELIZA prompted both scientists and the public to reconsider the potential of artificial intelligence.
Also read: Samsung to enhance Bixby virtual assistant with gen AI
Also read: Mercedes-Benz unveils AI-enhanced MBUX virtual assistant for personalized driving experience
The influence of ELIZA: Shaping the future of conversational AI
ELIZA’s introduction was a pivotal moment in the history of artificial intelligence, laying the groundwork for the development of modern conversational agents. Its innovative approach to mimicking human dialogue inspired a new generation of researchers and engineers to explore the possibilities of AI communication. Although ELIZA’s responses were generated through simple pattern-matching, the concept demonstrated that machines could engage in interactive and seemingly meaningful exchanges with humans.
One of ELIZA’s most significant impacts was on the public’s perception of AI. The program’s ability to simulate a therapeutic conversation led to what is now known as the “ELIZA effect.” This phenomenon refers to the tendency of people to attribute human-like understanding and emotions to machines based on their responses, regardless of the underlying technology’s simplicity. ELIZA’s success in creating this illusion highlighted the potential for AI to influence human emotions and perceptions.
In the decades following ELIZA’s introduction, the principles behind its design continued to influence the development of advanced conversational systems. Modern chatbots, virtual assistants, and AI-driven customer service tools owe a great deal to the foundational ideas established by ELIZA. While today’s technologies have far surpassed ELIZA in terms of complexity and capability, the pioneering work of Weizenbaum remains a crucial part of the conversation about AI and human interaction.
Reflecting on ELIZA’s legacy offers valuable insights into the evolution of conversational AI and the ongoing quest to understand and replicate human communication. As we advance in the field, ELIZA’s contributions remind us of the foundational ideas that continue to shape the future of technology.