- IANA allocates global IP address space and blocks to RIRs, and assigns AS numbers to organisations for routing on the Internet.
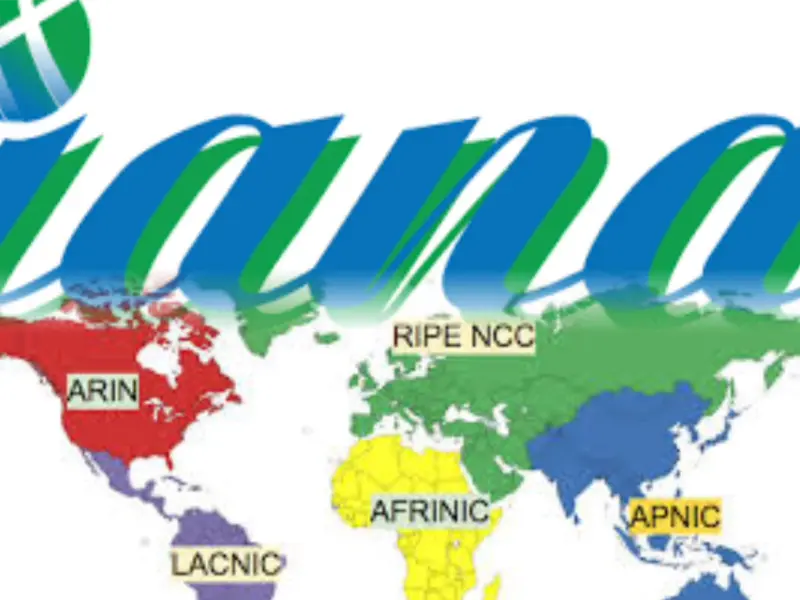
- RIRs, such as ARIN, RIPE NCC, APNIC, LACNIC, and AFRINIC, receive IP address allocations from IANA and further distribute them within their respective regions.
- But there is debate about whether the RIRs are still suitable for the role, considering the depletion of IPv4 addresses and the ever-increasing fees they demand.
The collaboration between the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and the Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) is essential for the efficient allocation of Internet number resources worldwide.
IANA functions
IANA operates under the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) and is responsible for managing global IP address space, AS number assignment, and protocol parameter allocation. IANA allocates IP address blocks to the five RIRs based on established global policies and guidelines.
These allocations are made from the unallocated address space maintained by IANA. IANA also oversees the delegation of top-level domains (TLDs) and country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) in the Domain Name System (DNS). IANA works closely with the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and other technical communities to ensure the smooth operation of Internet protocols and standards.
Regional Internet Registries
RIRs are independent organisations that currently hold the IP address registration database within specific geographic regions. Each RIR serves a designated region: ARIN for North America, RIPE NCC for Europe, the Middle East, and Central Asia, APNIC for the Asia-Pacific region, LACNIC for Latin America and the Caribbean, and AFRINIC for Africa. RIRs receive IP address allocations from IANA and further distribute these addresses to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), organisations, and end-users within their regions.
While the RIRs have developed and implemented regional policies for IP address allocation and registration to date, there is considerable debate about whether they are best suited for this role going forward.
Also read: RIPE internet registry faces losses, needs to increase fees, but how?
Collaboration and coordination
IANA and RIRs collaborate to ensure the accurate and efficient registration of Internet number resources. IANA delegates IP address blocks to RIRs based on global policies and the needs of each region. RIRs are responsible for implementing these allocations and ensuring that resources are used effectively.
RIRs collaborate with each other and with IANA to address issues such as IPv4 exhaustion, IPv6 adoption, and policy harmonisation across regions. The Number Resource Organisation (NRO) serves as the coordinating body for the RIRs, facilitating communication, cooperation, and coordination among the RIRs and with IANA.
Also read: Can Africa’s internet infrastructure cope with the future?
Policy development and community engagement
Both IANA and RIRs engage with the Internet community, including stakeholders from government, industry, academia, and civil society, to develop and implement policies that govern the allocation of Internet number resources.
Policy development processes within RIRs are meant to be open, transparent, and inclusive, allowing for input and participation from a diverse range of stakeholders. However in some examples, such as in AFRINIC, the RIR for Africa, and in APNIC, the RIR for Asia-Pacific, there have been examples of corruption and unfair and undemocratic practices taking place.
Is it necessary for IANA and RIRs to work together?
RIRs may face challenges in ensuring efficient use of the allocated IP address space. Issues such as address space fragmentation, underutilization of allocated resources, or hoarding of unused address blocks can affect the overall efficiency of address allocation and lead to a scarcity of addresses within a region.
Different regions may have different needs, priorities, and policies, which can lead to conflicts or disagreements in the allocation of IP address space. Ensuring smooth coordination and consistency between IANA and RIRs can therefore be a complex and ongoing process.