- As of October 2023, APNIC is close to completing the final delegation of IPv4 address blocks, signaling the exhaustion of available IPv4 resources in the Asia Pacific region.
- As a nonprofit Regional Internet Registry, APNIC manages IP address allocations and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs), ensuring the stable and efficient operation of the internet across the region.
In today’s digital age, the internet has become an indispensable part of everyday life, connecting billions of users across the globe. But behind the seamless connectivity and seemingly infinite access to information, there are systems and organizations working tirelessly to maintain and enhance the infrastructure that powers the web. One such key player is APNIC, the Asia Pacific Network Information Centre. This nonprofit organization plays a crucial role in managing the allocation of internet resources, including IP addresses and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs), in the Asia Pacific region. So, what exactly is APNIC, and why does it matter?
In this article, we will explore the core functions of APNIC, its historical significance, its role in addressing the growing demands of the internet, and its strategies for dealing with challenges like IPv4 exhaustion.

Also read: What to understand about APNIC IPv6 addresses?
Also read: APNIC launches new registry API to streamline network operations
What is APNIC? A regional internet registry
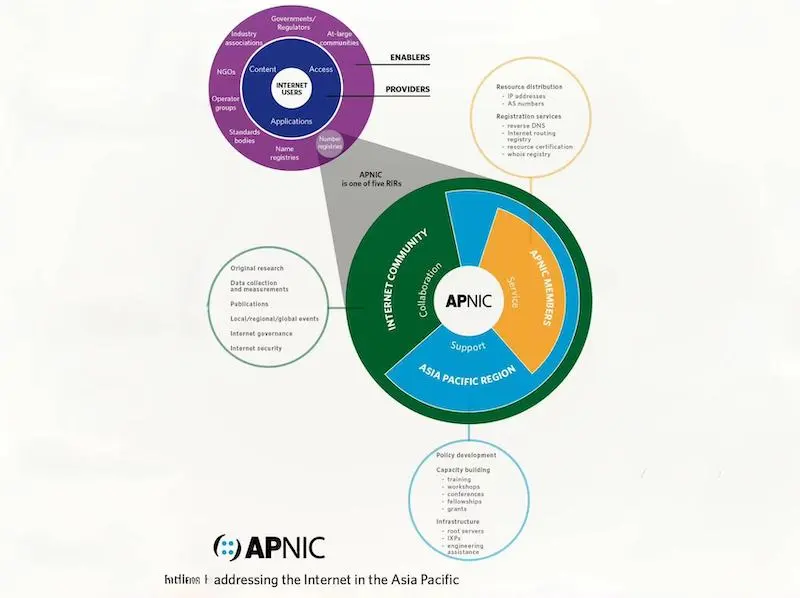
APNIC (Asia Pacific Network Information Centre) is one of the five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) globally, alongside AFRINIC, ARIN, LACNIC, and RIPE NCC. These RIRs are crucial in ensuring the efficient allocation of internet number resources, including IP addresses and ASNs, to network operators across their respective regions.
APNIC‘s role is particularly vital because the Asia Pacific region hosts a significant portion of the world’s internet infrastructure, with rapid technological growth and millions of new users coming online each year. This growing digital landscape makes the management of internet resources more critical than ever. As Geoff Huston, chief scientist at APNIC, explains, “The Asia Pacific region is experiencing unparalleled growth, and managing internet resources effectively ensures that this expansion is sustainable and equitable.”
Huston further emphasizes that, “APNIC’s responsibility is not just about allocation; it’s about shaping the future of the internet in a way that supports regional growth while fostering global interoperability.” This highlights APNIC’s unique role as a bridge between the global and regional internet landscapes, ensuring a seamless and efficient distribution of essential internet resources.
APNIC’s responsibility is not just about allocation; it’s about shaping the future of the internet in a way that supports regional growth while fostering global interoperability.
Geoff Huston, chief scientist at APNIC
Also read: Jia Rong Low becomes APNIC’s new director general
How does APNIC work?

APNIC does not own IP addresses. Instead, it acts as an intermediary that receives allocations of IP address blocks from the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), the global body responsible for managing the distribution of internet number resources. APNIC then allocates these IP address blocks to its members, which include internet service providers (ISPs), national internet registries (NIRs), network information centers (NICs), and various other organizations across the Asia Pacific region.
This allocation process is governed by well-defined policies designed to ensure the efficient, equitable, and sustainable distribution of internet resources. According to Dr. Kuo-Wei Wu, a prominent figure in internet governance, “The efficiency of regional registries like APNIC is critical to the global operation of the internet. By managing resources locally, APNIC helps ensure that infrastructure development is aligned with regional needs while maintaining the global internet’s interoperability.”
Dr. Wu further highlights the importance of APNIC’s transparent allocation process, stating, “The role of APNIC is not just about distributing addresses; it is about managing the foundation upon which the internet continues to grow. The careful regulation of these resources helps avoid fragmentation and promotes collaboration within the region.”
These expert insights reflect the vital role of APNIC in ensuring the region’s internet infrastructure can expand sustainably, supporting a growing number of users and technologies while maintaining global connectivity standards.
The efficiency of regional registries like APNIC is critical to the global operation of the internet. By managing resources locally, APNIC helps ensure that infrastructure development is aligned with regional needs while maintaining the global internet’s interoperability.
Dr. Kuo-Wei Wu, a prominent figure in internet governance
Also read: APNIC strengthens collaboration at KRNOG 2.0 in Seoul
Also read: APNIC fosters collaboration at Peering Asia 6.0
APNIC’s key functions
While APNIC’s primary role is to allocate IP addresses and ASNs, its functions extend far beyond this basic task. Let’s take a look at the key responsibilities that APNIC undertakes to ensure the smooth functioning of the internet in the Asia Pacific region.

1. IPv4 and IPv6 allocation
One of APNIC’s most critical functions is the allocation of both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. With the global depletion of IPv4 addresses, this task has become increasingly complex and vital for the continued expansion of the internet.
- IPv4 Allocation: The IPv4 address space, which has been in use for decades, is gradually running out due to the increasing number of internet-connected devices. APNIC plays a crucial role in managing this dwindling resource by allocating smaller IPv4 address blocks to network operators, ensuring that the transition to IPv6 is as smooth as possible.
- IPv6 Allocation: IPv6 is the next generation of internet addressing, designed to overcome the limitations of IPv4. APNIC is actively promoting IPv6 adoption and supporting network operators in transitioning to this new protocol. IPv6 provides an almost infinite number of IP addresses, allowing for the continued growth of the internet in the Asia Pacific region and beyond.

2. Whois database administration
Another important function of APNIC is the administration of the Whois database. This publicly accessible database contains information about the ownership and allocation of IP addresses and ASNs. It is a critical tool for network operators, researchers, and law enforcement agencies to track and trace internet resources, ensuring that any misuse or abuse of the internet can be quickly identified and addressed.
The Whois database also helps ensure transparency in internet governance by making it easy for anyone to access information about IP address allocations.
3. Reverse DNS management
APNIC also manages reverse DNS (Domain Name System) for the IP addresses it allocates. Reverse DNS allows users to query an IP address and retrieve the associated domain name, a vital process for ensuring the smooth operation of the internet. This function plays a key role in network troubleshooting, email validation, and security functions such as spam prevention, where verifying the legitimacy of incoming communications is crucial.
Dr. Lixia Zhang, a recognized expert in internet infrastructure, points out that “Reverse DNS is a cornerstone for maintaining trust on the internet. By ensuring that IP addresses can be mapped back to their domain names, APNIC helps verify the authenticity of data exchanges, which is vital for cybersecurity.”
In a similar vein, Dr. William S. Davenport, a leading researcher in network security, underscores the importance of reverse DNS in combating malicious activity: “Effective reverse DNS management not only aids in troubleshooting but also acts as an important tool in detecting fraudulent IP addresses used for spam or other forms of cyberattack. APNIC’s role in overseeing this process adds an extra layer of trust and security to the Asia Pacific region’s internet infrastructure.”
Effective reverse DNS management not only aids in troubleshooting but also acts as an important tool in detecting fraudulent IP addresses used for spam or other forms of cyberattack. APNIC’s role in overseeing this process adds an extra layer of trust and security to the Asia Pacific region’s internet infrastructure.
Dr. William S. Davenport, a leading researcher in network security
4. Research and development
APNIC is also deeply involved in research and development to address critical issues related to internet infrastructure. Some of the key areas of focus include:
- IPv4 depletion: APNIC has been working on policies to manage the remaining IPv4 address space effectively and help organizations transition to IPv6.
- Security: APNIC works on initiatives to enhance the security of internet resources, ensuring that the internet infrastructure remains safe from malicious actors.
- Internet policy development: APNIC plays an active role in the global dialogue around internet governance and policy development, helping to shape the future of the internet.
The history of APNIC: From pilot project to global authority
APNIC’s journey began on January 15, 1993, when it was established as a pilot project in Japan with the goal of supporting network operations and resource registration for the Asia Pacific region. The initial purpose was to help manage IP address allocation in the region, which was rapidly growing due to the increasing number of internet-connected networks and devices.
In 1998, after its initial success, APNIC officially moved its headquarters to Brisbane, Australia, and registered as a nonprofit organization. This move allowed APNIC to better serve its growing membership and solidify its role as the central body responsible for managing internet resources in the Asia Pacific region.
Today, APNIC serves nearly 8,000 members, including ISPs, governments, academic institutions, and other stakeholders across 56 economies. Its governance structure includes a bottom-up policy development process, ensuring that all members have a voice in shaping the policies and strategies that guide APNIC’s operations.
Challenges faced by APNIC
Like many organizations that manage critical internet infrastructure, APNIC faces a number of challenges as the internet continues to grow and evolve. One of the most pressing challenges is the depletion of IPv4 addresses.

IPv4 exhaustion
In 2011, the world reached a milestone in internet history: IPv4 address exhaustion. With billions of devices being connected to the internet every year, the 32-bit address space of IPv4 was simply no longer sufficient to accommodate the growing number of internet-connected devices.
APNIC has been at the forefront of addressing this issue by working to allocate the remaining IPv4 address blocks in a fair and efficient manner. However, as of October 2023, APNIC is nearing the completion of its IPv4 allocation, meaning that it will soon run out of IPv4 addresses altogether.
The transition to IPv6
As APNIC nears the end of its IPv4 allocation, the organization is increasingly focused on promoting the adoption of IPv6. IPv6, with its 128-bit address space, provides a vastly larger pool of IP addresses, making it the only viable solution for the growing demand for internet-connected devices. APNIC is working tirelessly to help network operators transition to IPv6 by providing technical assistance, policy support, and resources.
Other industry challenges
Beyond IPv4 exhaustion, APNIC faces other challenges related to security, network abuse, and the growing complexity of internet governance. To address these issues, APNIC continues to invest in research and development and collaborate with other organizations to enhance the overall security and stability of the internet infrastructure.
APNIC’s impact on the Asia Pacific region
The Asia Pacific region is home to nearly half of the world’s internet users, and this number continues to grow. As the digital economy expands in this region, the role of APNIC becomes even more critical. By managing the allocation of IP addresses and ASNs, APNIC ensures that the internet infrastructure in the Asia Pacific region remains robust, scalable, and secure.
APNIC’s work also supports the growth of new technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G, and artificial intelligence, all of which rely on a stable and efficient internet infrastructure. By helping to shape the future of the internet in the Asia Pacific region, APNIC plays a vital role in supporting the digital transformation of economies, governments, and societies.
APNIC and the future of the internet

As the internet continues to evolve, APNIC‘s role as a Regional Internet Registry becomes ever more important. From managing IP address allocation to supporting the transition to IPv6, APNIC is essential in ensuring the continued growth and stability of the internet in the Asia Pacific region.
With its commitment to transparency, research, and community involvement, APNIC is not only helping to manage the internet resources of today but also laying the foundation for the internet of tomorrow. As the digital landscape becomes more complex, APNIC’s work will remain a crucial pillar in supporting the efficient, secure, and scalable operation of the global internet.
FAQ
APNIC (Asia Pacific Network Information Centre) is a nonprofit organization that manages the allocation of IP addresses and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs) across the Asia Pacific region. It acts as a Regional Internet Registry (RIR), ensuring efficient distribution of internet resources, supporting the stable operation of the internet infrastructure, and promoting regional growth.
APNIC receives allocations of IP address blocks from the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). It then distributes these resources to its members, which include internet service providers (ISPs), national internet registries (NIRs), and network operators. The allocation process is governed by strict policies to ensure fairness, sustainability, and global interoperability.
With the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, APNIC has been focusing on promoting the adoption of IPv6 to ensure continued growth of the internet. IPv6 offers a virtually unlimited number of addresses, providing a long-term solution to the depletion of IPv4 resources. APNIC plays a key role in guiding and supporting the region’s transition to IPv6.
APNIC manages reverse DNS for the IP addresses it allocates, which is essential for verifying the legitimacy of internet traffic and preventing malicious activity such as spam or fraud. By overseeing this process, APNIC contributes to maintaining the trust and security of the internet infrastructure in the Asia Pacific region.
Organizations in the Asia Pacific region, such as ISPs, NIRs, and network operators, can apply for membership with APNIC to receive IP address allocations and ASNs. Membership provides access to APNIC’s resources, tools, and services, including technical support and policy development opportunities. Interested parties can apply through the APNIC website.

