- AI robots combine artificial intelligence with robotics, enabling machines to perform complex tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously by processing information, learning from experiences, and making decisions based on AI algorithms.
- AI robots are utilised across various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, logistics, and defense, significantly improving efficiency, precision, and safety in tasks such as assembly, surgery, crop monitoring, and hazardous environment operations.
- The future of AI robots looks promising with advancements in AI and machine learning, improved human-robot collaboration, and enhanced sensing capabilities. However, challenges such as high development costs, ethical concerns, technical limitations, and security risks need to be addressed to fully realise their potential.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics are two of the most transformative technologies of our time. When combined, they give rise to AI robots—machines that can perform tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously by processing information and making decisions based on AI algorithms. These robots are designed to interact with their environment and perform a variety of tasks, from simple repetitive actions to complex problem-solving activities. This blog will explore what AI robots are, how they work, their applications, benefits, challenges, and the future prospects of this fascinating field.
Understanding AI robots
AI robots are machines that integrate artificial intelligence with robotics to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI enables these robots to learn from their experiences, adapt to new situations, and perform tasks more efficiently over time. Here’s a breakdown of the key components that make up an AI robot:
Artificial intelligence
AI provides the cognitive functions required for robots to process data, recognise patterns, and make decisions. AI can be divided into several subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and more.
Robotics
Robotics involves the design, construction, and operation of robots. It encompasses various disciplines such as mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and computer science to create machines capable of performing tasks in the physical world.
Sensors and actuators
Sensors collect data from the robot’s environment, such as visual, auditory, and tactile information. Actuators, on the other hand, enable the robot to interact with its environment by moving parts or performing actions.
Control systems
These systems process the data collected by sensors and use it to make decisions, controlling the robot’s movements and actions.
How AI robots work
AI robots operate by following a cycle of perception, processing, and action:
Perception
The robot uses sensors to gather data from its environment. This can include cameras for vision, microphones for sound, touch sensors, and more. Advanced AI robots use a combination of these sensors to create a comprehensive understanding of their surroundings.
Processing
The data collected by the sensors is processed using AI algorithms. For instance, machine learning models can analyse visual data to recognise objects, while natural language processing algorithms can interpret and generate human language. This step involves interpreting the sensory data and making decisions based on pre-programmed rules or learned patterns.
Action
Based on the processed information, the robot performs an action using its actuators. This could involve moving to a different location, picking up an object, or generating a verbal response.
Also read: AI robots with super vision power ‘groundbreaking’ warehouse
Applications of AI robots
AI robots are used across various industries and applications, demonstrating their versatility and potential. Here are some notable examples:
Manufacturing
AI robots are widely used in manufacturing for tasks such as assembly, welding, painting, and quality control. They improve efficiency, precision, and safety in production lines.
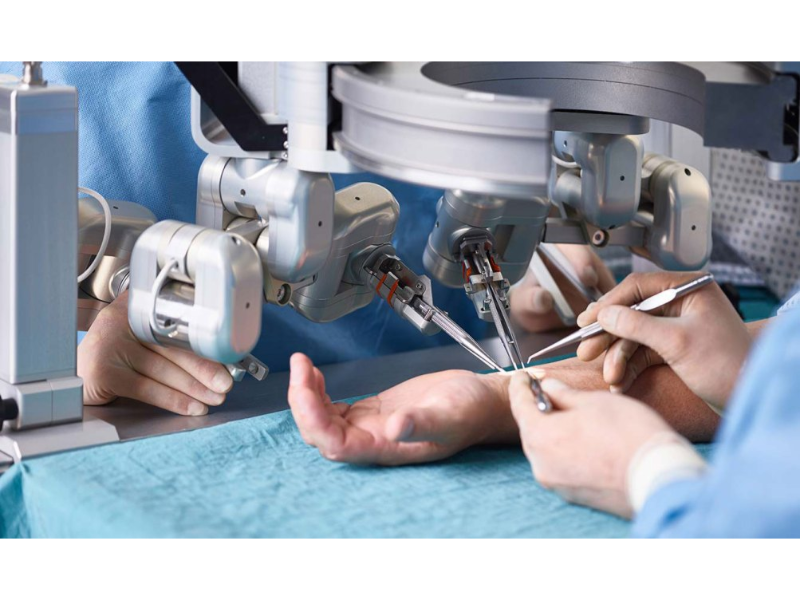
Healthcare
In healthcare, AI robots assist in surgeries, patient care, and rehabilitation. Surgical robots can perform minimally invasive procedures with high precision, while assistive robots help patients with mobility and daily activities.
Service industry
Robots in the service industry perform tasks like cleaning, delivery, and customer service. For example, autonomous vacuum cleaners and delivery robots in hotels and restaurants enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
Agriculture
AI robots in agriculture are used for planting, harvesting, monitoring crop health, and managing livestock. These robots increase productivity and reduce the need for manual labor.
Exploration
Robots equipped with AI are used in space and underwater exploration. They can operate in extreme environments, collect data, and perform tasks that are dangerous or impossible for humans.
Logistics and warehousing
AI robots streamline logistics and warehousing operations by automating tasks such as sorting, packaging, and transporting goods. This leads to faster and more accurate order fulfillment.
Military and defense
In the military, AI robots are used for surveillance, reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and search and rescue missions. They enhance safety and operational efficiency in challenging and hazardous environments.
Benefits of AI robots
The integration of AI with robotics brings several benefits:
Efficiency and productivity
AI robots can perform repetitive and labor-intensive tasks faster and more accurately than humans, leading to increased productivity and operational efficiency.
Precision and accuracy
AI algorithms enable robots to perform tasks with high precision, reducing errors and improving the quality of outcomes, especially in fields like manufacturing and healthcare.
Safety
Robots can operate in dangerous environments, handling hazardous materials and performing tasks that would pose risks to human workers. This enhances workplace safety.
Cost savings
Over time, the use of AI robots can lead to significant cost savings by reducing labor costs, minimising errors, and improving process efficiencies.
Scalability
AI robots can easily be scaled to meet increasing demands. For example, in manufacturing, additional robots can be integrated into production lines to increase output without compromising quality.
Challenges of AI robots
Despite their numerous advantages, AI robots also face several challenges:
Complexity and cost
Developing and deploying AI robots is complex and expensive. The initial investment in technology, infrastructure, and training can be substantial.
Ethical and social concerns
The widespread use of AI robots raises ethical and social issues, such as job displacement, privacy concerns, and the potential for misuse in surveillance or military applications.
Technical limitations
While AI and robotics have advanced significantly, there are still technical limitations. Robots may struggle with tasks requiring high levels of dexterity, adaptability, or understanding of nuanced human behaviors.
Security risks
AI robots can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could compromise their functionality and lead to significant security breaches, especially in critical applications like healthcare and defense.
Regulatory and compliance issues
The integration of AI robots into various sectors must comply with existing regulations and standards, which can vary significantly across regions and industries.
Also read: Automakers Magna to trial Sanctuary AI’s humanoid robots
The Future of AI robots
The future of AI robots is promising, with continuous advancements in technology driving new possibilities. Here are some trends and potential developments:
Advancements in AI and ML
Ongoing research in AI and machine learning will lead to more sophisticated and capable robots. Enhanced algorithms will enable better decision-making, learning, and adaptability.
Human-robot collaboration
Future AI robots will work more closely with humans, complementing their skills and performing tasks that require a combination of human intuition and robotic precision. This collaborative approach will enhance productivity and innovation.
Autonomous systems
The development of fully autonomous robots that can operate independently in complex and dynamic environments is a key focus area. These robots will revolutionise industries like transportation, logistics, and exploration.
Improved interoperability
Efforts to standardise communication protocols and interfaces will improve the interoperability of AI robots, enabling seamless integration into existing systems and workflows.
Enhanced sensing and perception
Advances in sensor technology and perception algorithms will enable robots to better understand and interact with their environments, leading to more effective and efficient operations.
Ethical AI and governance
As AI robots become more prevalent, there will be a greater emphasis on ethical AI and governance. This includes developing frameworks and guidelines to ensure the responsible and fair use of AI robots.
AI robots represent a significant leap forward in the capabilities of machines to perform complex tasks autonomously. By combining the cognitive abilities of AI with the physical capabilities of robotics, these machines are transforming industries, enhancing productivity, and improving safety. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of AI robots are immense, and their continued development promises to bring even more innovative solutions to the forefront. As we navigate the ethical, social, and technical challenges, the future of AI robots looks bright, with endless possibilities for enhancing our world.

