- XAI stands for Explainable Artificial Intelligence.
- It refers to the ability of AI systems to provide transparent and understandable explanations for their decisions and actions.
- XAI addresses the “black box” problem in AI, enhancing trust, accountability, and human understanding of AI systems.
- Note that xAI is also an artificial intelligence startup owned by Elon Musk.
Explainable Artificial Intelligence, abbreviated as XAI, has emerged as a crucial concept in artificial intelligence (AI). As the name suggests, XAI focuses on making AI systems explainable and transparent, allowing users to understand how they arrive at their decisions.
Definition and purpose of XAI
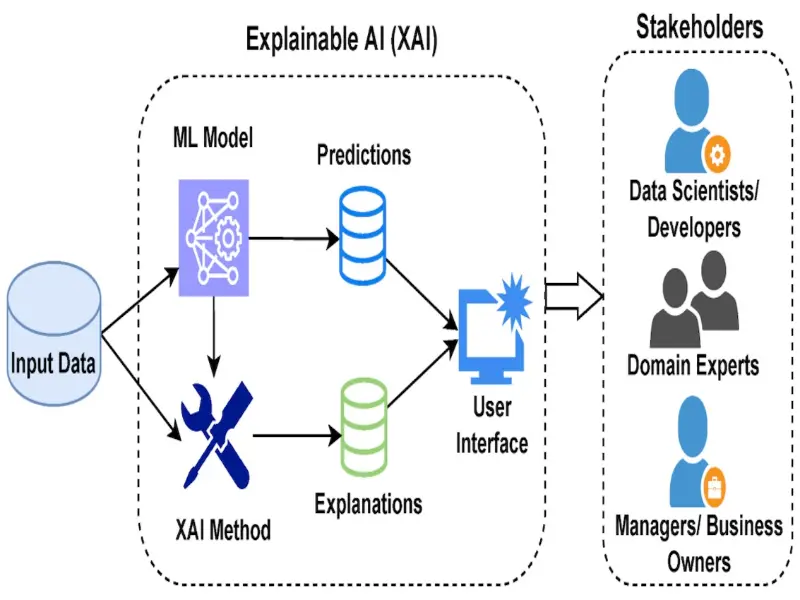
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) refers to the capability of AI systems to provide clear, understandable explanations for their decisions and behaviors.
The primary purpose of XAI is to demystify the “black box” nature of AI algorithms, enabling users to comprehend how AI arrives at specific outcomes or recommendations.
By enhancing transparency and interpretability, XAI promotes trust, accountability, and user acceptance of AI technologies in critical decision-making processes.
Also read: Inside the Black Box: Demystifying AI Models
Challenges and opportunities in XAI implementation
Despite its importance, implementing XAI poses several challenges, particularly in complex AI models such as deep neural networks, where decision-making processes are highly intricate.
One of the key challenges is balancing the trade-off between model complexity and interpretability, as more sophisticated models often sacrifice explainability for improved performance.
However, advancements in XAI techniques, such as model-agnostic approaches, interpretable model architectures, and post-hoc explanation methods, offer promising avenues for addressing these challenges.
Also read: What does Mistral AI do?
Applications of XAI across industries
In the healthcare sector, XAI plays a crucial role in assisting medical professionals in interpreting AI-driven diagnostic tools and treatment recommendations. For example, companies like Merative L.P., formerly IBM Watson Health are developing XAI solutions to explain the rationale behind AI-generated clinical insights, empowering clinicians to make informed decisions.
In finance, XAI is utilised to enhance the transparency and accountability of AI-driven algorithms in risk assessment, fraud detection, and investment strategies. Firms like Capital One leverage XAI techniques to provide customers with understandable explanations for credit decisions and financial advice.
In autonomous vehicles and robotics, XAI ensures that AI systems can justify their actions and responses in real-time scenarios, enhancing safety and reliability. Companies like Waymo integrate XAI capabilities into their self-driving cars to provide clear explanations for navigation decisions and hazard detection.
Also read: Anthropic’s AI now connects with external applications in real time
The role of XAI in ethical AI development
XAI serves as a critical tool for identifying and mitigating biases inherent in AI models, thereby promoting fairness and equity in decision-making processes. By providing transparent explanations for AI predictions, XAI enables stakeholders to detect and rectify instances of algorithmic bias, ensuring that AI systems uphold ethical principles and do not perpetuate discriminatory outcomes.
Transparent explanations provided by XAI instill confidence and trust in AI systems among end-users, fostering greater acceptance and adoption of AI-driven technologies. When users understand the rationale behind AI recommendations or decisions, they are more likely to trust the system and rely on its outputs in critical domains such as healthcare, finance, and public safety.
XAI facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements related to AI transparency and accountability, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. By providing interpretable explanations for AI decisions, organisations can demonstrate compliance with legal and ethical standards, reducing the risk of regulatory scrutiny and potential liabilities associated with opaque AI systems.