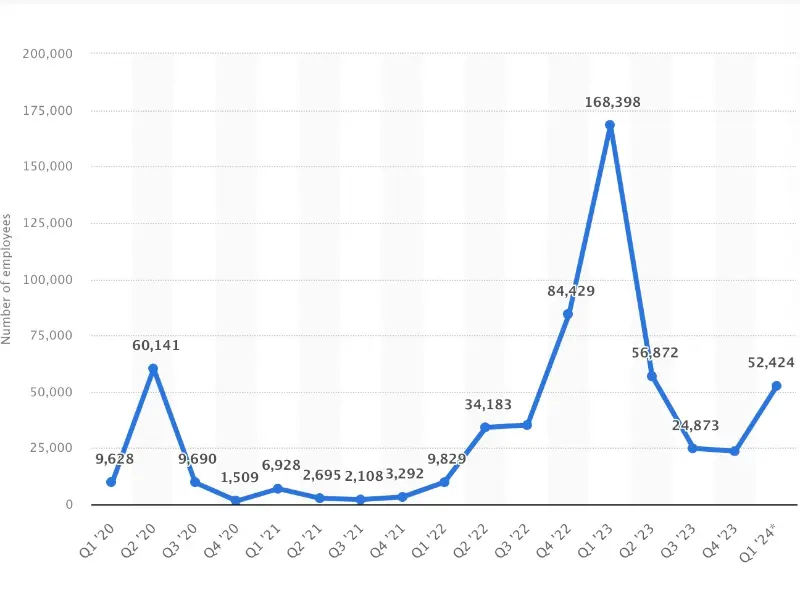
- The tech industry saw a notable downturn in the final quarter of 2022, with over 70,000 employees worldwide being laid off.
- The situation escalated dramatically in the first quarter of 2023, with a record high of 167.4 thousand tech sector employees losing their jobs.
- Despite improving fundamentals, tech layoffs have persisted into 2024. Companies continue to restructure and streamline operations, leading to further workforce reductions.
The tech industry, often heralded for its rapid growth and innovation, also experiences its fair share of setbacks. One such setback is the occurrence of layoffs, which can send shockwaves through both the industry and the broader economy. Understanding when these layoffs began and their subsequent impact is crucial for navigating the ever-evolving landscape of technology and employment.
When did tech layoffs start?
In the final quarter of 2022, technology firms globally witnessed a substantial workforce reduction, with more than 70,000 employees being let go. It is reported that Meta cut 11,000 jobs, Twitter cut 3,700, Stripe cut 1,100, Microsoft cut 1,000, etc.
However, the situation escalated dramatically in the first quarter of 2023, marking a record high in tech sector layoffs, with an astounding 167,400 employees losing their jobs. Major industry players such as Google, Microsoft, Meta, and IBM all contributed to this surge. Amazon notably conducted two separate rounds of layoffs within this timeframe. Industries hit hardest included consumer goods, hardware, food, and healthcare. Prominent companies that implemented significant staff reductions include Flink, Getir, Booking.com, Uber, PayPal, LinkedIn, and Peloton, among others.
Despite initial hopes for recovery, the tech industry continued to grapple with layoffs well into 2024. Companies across various sectors, from consumer goods to healthcare, faced the harsh reality of downsizing amidst economic uncertainties. Startups and established firms alike found themselves compelled to streamline operations, resulting in workforce reductions despite improving market fundamentals.
Also read: Dell layoffs hit 13,000 in 2023, double the number claimed
Factors driving tech layoffs
Fluctuations in market conditions, exacerbated by global events and geopolitical tensions, have played a significant role in precipitating tech layoffs. Economic downturns or uncertainties often prompt companies to reevaluate their staffing needs and implement cost-saving measures, including workforce reductions.
Rapid technological advancements, while driving innovation, can also disrupt established business models and industries. Companies facing obsolescence or struggling to adapt to emerging trends may resort to layoffs as part of broader restructuring efforts to remain competitive.
Strategic realignments, mergers, acquisitions, and divestitures can all necessitate workforce adjustments as companies seek to streamline operations and optimise resources. Shifts in corporate priorities or leadership changes may also prompt organisational restructuring, resulting in layoffs as redundant roles are eliminated or consolidated.
Also read: Reasons behind mass layoffs at tech companies
Impact on employees and the industry
Layoffs can have profound psychological and financial implications for affected employees, leading to increased stress, anxiety, and uncertainty about future prospects. The pervasive fear of layoffs can also undermine employee morale and productivity, hindering innovation and collaboration within organisations.
Tech layoffs risk depleting the industry’s talent pool as skilled professionals seek opportunities elsewhere or opt for alternative career paths. The loss of experienced employees and specialised expertise can impede companies’ ability to innovate and adapt to evolving market demands, potentially eroding their competitive edge.
Tech layoffs reverberate beyond individual companies, affecting supply chains, local economies, and broader industry ecosystems. Displaced workers may struggle to find comparable employment opportunities, leading to increased unemployment rates and socioeconomic disparities within affected communities.