- Tesla’s stock has declined by about 30% in 2024, with forecasts suggesting lower vehicle deliveries and decreasing profit expectations. Investors come to the question, “Is Tesla a good stock to buy?”.
- Despite challenges, Tesla continues to innovate, focusing on Model 2, FSD 12, and the 4680 battery to drive future growth.
- While facing market uncertainties, Tesla maintains a strong position in the EV charging market, insurance business, and solar energy sector, supported by robust financials and optimistic projections from Wall Street analysts.
Tesla stock is down approximately 30% in 2024, with analysts forecasting that 2024 vehicle deliveries might be lower than last year’s total, and profit forecasts are decreasing before first-quarter earnings.
After closing the chapter on 2023, the Wall Street consensus indicates that Tesla’s earnings for 2024 are expected to be significantly lower than the previous year, indicating another year of decline for this growth-oriented stock. Analysts presently anticipate Tesla’s earnings per share to be only $2.70 in 2024, a decrease of over 13% compared to $3.12 in 2023, according to FactSet.
Wall Street’s consensus estimates for Tesla’s EPS in 2024 have dropped by 30% since the end of 2023. With Tesla set to report earnings on April 23, analysts are likely just starting to revise their earnings forecasts downward.
Looking ahead, the consensus among Wall Street analysts is that Tesla’s EPS in 2025 will be $3.70, down from the projection of $5.29 at the end of 2023, as reported by FactSet.
While analysts await Q1 earnings and updates on EV demand and auto gross margins, the primary concern for investors remains: Is Tesla a good stock to buy?
Also read: What AI voice generator is everyone using?
Also read: The tech names in Time’s 100 Most Influential People of 2024 list
Tesla’s 2023 Q4 financial report doesn’t meet the expectations
Previously, Tesla turned in a lackluster “report card.” According to the company’s Q4 financial report, in Q4 2023, Tesla delivered 484,500 vehicles, reaching a historic high; with a yearly delivery of 1.8086 million vehicles, a YoY increase of 38%, “last-minute” achieving Musk’s annual delivery goal.
Due to past glory, investors have high expectations for Elon Musk and Tesla. This report did not meet their expectations. After the financial report was released, Tesla’s stock price fell by 12.13% in a single day, marking the largest single-day decline since 2020. Even at the time of writing, Tesla’s stock price continued to fall by over 8% to $187 compared to before the financial report was released, with the latest total market value at $594.1 billion.
From a financial perspective, Tesla’s sales targets were achieved as planned, with total revenue reaching a new high, which should be cause for celebration. However, the slowing revenue growth and continuous decline in gross margin have disappointed Wall Street. Tesla’s gross margin in Q4 2023 fell to 17.6%, with an operating profit margin of 8.2%, falling back to the average level of the automotive industry; although net profit reached $7.9 billion, this was mainly due to a one-time $5.9 billion non-cash tax refund.
At the same time, Tesla’s guidance for 2024 is also somewhat disappointing, with sales growth expected to be significantly lower than the 38% in 2023, further increasing the uncertainty faced by Tesla.
In terms of delivery volume, Tesla passed the mark. With an annual delivery of 1.8 million vehicles and 484,500 deliveries in Q4, marking a 19.5% YoY increase.
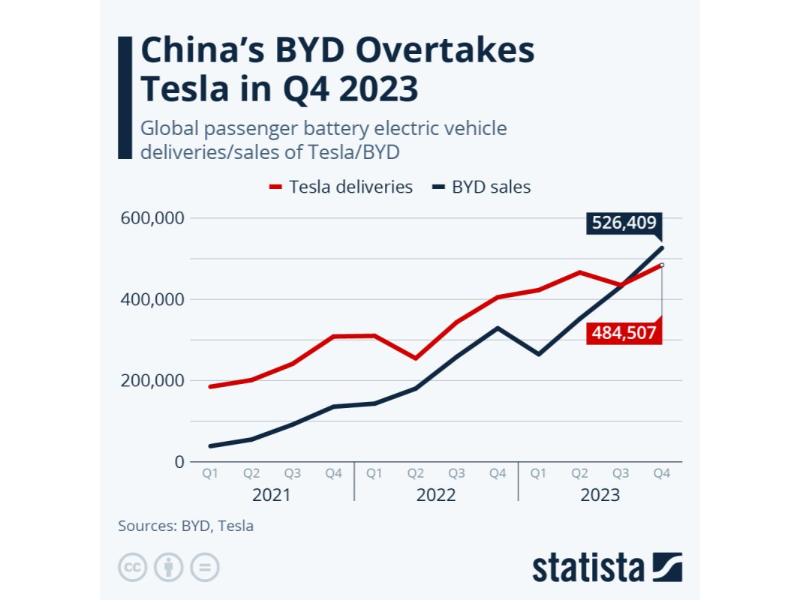
Despite setting a delivery record, Tesla lost its position as the world’s largest electric vehicle manufacturer in Q4 to BYD. BYD achieved a quarterly sales volume exceeding Tesla for the first time with 520,000 deliveries. However, Tesla’s December sales of domestically manufactured electric vehicles in China grew by nearly 70%.
While this threat is undeniable, prompting Musk to call for trade barriers to prevent Chinese electric vehicle companies from outperforming others globally, Tesla has shown readiness to address the challenge by upgrading the Model Y and reducing prices.
Tesla follows a “boutique route” model
It is well-known that Tesla follows a “boutique route” model, positioning similar to Apple phones. It currently offers only five models, with the Model 3 and Model Y being the mainstays, covering price ranges mainly from $30,000 to $60,000. The higher-priced Model S, Model X, and Cybertruck have a relatively smaller impact on sales. This product positioning to some extent limits Tesla’s penetration in broader markets.
While the Chinese new energy vehicle market is rapidly developing, new energy vehicles in overseas markets face severe challenges such as high inflation and declining market demand. This poses a significant challenge for Tesla, which has a high degree of internationalisation.
Meanwhile, overseas buyers still hold a wait-and-see attitude towards pure electric vehicles due to high prices and concerns about charging convenience and range anxiety, discouraging many consumers.
It is worth noting that the world’s largest car rental company, Hertz, plans to sell about 20,000 electric vehicles, accounting for a third of its electric vehicle fleet, due to high maintenance costs and lower-than-expected resale value of electric vehicles. This is a significant shift in direction for Hertz, which pledged to purchase 100,000 Tesla vehicles in 2021.
Tesla’s future hinges on three main pillars: Model 2, FSD 12, and the 4680 battery

Elon Musk explained, “We’re currently between two major growth waves. We’re focused on ensuring the next one is well executed, driven by next-gen cars, energy storage, full self-driving, and other projects.”
Tesla’s next-gen car, planned to be produced at the Austin Gigafactory, will be called Model 2, priced around $25,000, aiming to be one of the most affordable battery electric vehicles (BEVs). However, whether its actual cost will be as low as $25,000 remains to be seen, as Musk’s and Tesla’s commitments often exceed actual outcomes.
The significance of the Model 2 lies more in its manufacturing process than its impact on the BEV market. The so-called “super casting” technology aims to replace traditional methods of welding metal parts into integrated bodies, with potential significant cost savings.
Launching the Model 2 into the market at a relatively moderate price and generating revenue is not easy, even for Musk himself.
While Tesla is hailed as a top global pure electric vehicle manufacturer, its software prowess in the automotive industry is not adequately recognized outside the industry, with competitors striving to catch up. Tesla is a pioneer in centralized vehicle computing and a key driver of over-the-air (OTA) software updates—all forming the latest buzzword in the industry: “software-defined cars.”
In the near future, automakers will increasingly offer certain vehicle features through subscriptions, which can be added or removed via OTA, creating additional revenue opportunities beyond initial sales or leases.
Tesla’s latest Full Self-Driving (FSD) software, FSD12, can be activated via OTA. The current FSD11 suite is priced at up to $15,000. FSD12 is undergoing beta testing by Tesla employees and a small number of customers, with early feedback being positive but with some complaints.
The launch of FSD12 is significant as Tesla shifts from a computer code system written by humans as the basis for autonomous driving to an artificial intelligence or machine learning system. Tesla’s Dojo supercomputer uses millions of visual images extracted from real driving of Tesla vehicles to train FSD12.
Musk envisions a world full of autonomous Tesla vehicles—robot taxis without steering wheels and other controls earning money for owners—but that day has not yet come. Although Tesla’s recent pivot towards artificial intelligence may prove to be another significant step in that direction, some enthusiasts of autonomous driving purchasing vehicles equipped with FSD12 also support this grand vision.
Analysts say FSD could generate annual revenue in the billions
Goldman Sachs analysts have estimated that FSD could generate annual revenue in the billions and potentially more in the coming years.
The third key pillar on which Tesla’s financial performance depends is its 4680 lithium-ion battery, which replaces its previous batteries and was first unveiled in September 2020 and has been rolling out since. The 4680 refers to the cylindrical dimensions of 46 mm x 80 mm, which is becoming the new industry standard and is being used by other manufacturers (including BYD). The new battery is an essential part of Tesla’s Cybertruck powertrain.
According to Chinese battery company Evlithium, Tesla’s 4680 battery offers higher power density, energy density, better thermal performance, and lower cost compared to its predecessor.
One of the biggest challenges with advanced batteries is manufacturing processes. Very small defects can lead to overheating, power degradation, and unsuitability for vehicle use. During the latest earnings call, Tesla executives stated that progress in battery production ramp-up is progressing smoothly, crucial for meeting Cybertruck demand.
Is Tesla a good stock to buy?
After analysing the significant drop in Tesla’s stock price, let’s examine whether the company itself still holds investment value.
Tesla ranks second in the US for charging infrastructure, with 33,000 charging points, primarily consisting of Level 3 chargers, making it a dominant player in the electric vehicle (EV) charging market. This segment is expected to see a significant 36% growth rate, reflecting the increasing demand for EVs nationwide.
Regarding Tesla’s potential revenue sources, its insurance business has promising prospects, forecasted to contribute up to 30% of company profits. Despite initial challenges like website crashes upon launch and relying on vehicle data for safety ratings to determine premiums, some speculate Tesla’s insurance business could generate around $250 billion in revenue at some point. Currently, the global automotive insurance market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 7.38%.
Additionally, Tesla ventures into solar energy, offering products such as solar panels, solar roofs, string inverters, and batteries, with global growth expected to reach 6.9% by 2029.
Tesla boasts a healthy financial condition
Tesla boasts a healthy financial condition. Total debt is decreasing at an annual rate of -9.5%, while cash reserves are skyrocketing by 127.3% annually—a remarkable feat rare in capital-intensive industries. From the second quarter of 2023 to the fourth quarter of 2023, cash reserves grew by 26%, while total debt decreased by about 10%.
Moreover, free cash flow (FCF) has been increasing at a rate of 59.6% annually since 2017. In my previous articles, this metric was $5.1 billion, but it soared to $9.5 billion subsequently, marking an 86% growth. However, it’s worth noting that this significant increase is largely attributed to a $5.7 billion tax benefit.
The free cash flow margin naturally rose from 5.5% to 9.8%, closer to the profit margins recorded since 2020.
Wall Street analysts believe Tesla’s fair value is expected to be $311.12, with an upside potential of 67%. Additionally, if the equity component continues to grow at the same rate observed from 2017 to 2023, the future price of the stock could reach approximately $666.51. This forecast implies an annual return rate of around 43% by 2029.

