- The rise of deepfake technology poses unique challenges and opportunities in political campaigns, with varying impacts in the US and India.
- While deepfakes can increase engagement and drive fundraising efforts, they also threaten the integrity of democratic processes through misinformation.
OUR TAKE
Deepfake technology is revolutionising political campaigns by enhancing engagement and fundraising, but it also introduces serious risks to democracy. The potential for misinformation and voter manipulation is significant, making it essential for governments and tech companies to collaborate on regulations and detection tools to safeguard electoral integrity.
— Zoey Zhu, BTW media
Deepfake technology, which utilises artificial intelligence to create hyper-realistic but entirely fabricated videos, has rapidly evolved into a potent tool in the realm of political propaganda. Originally emerging as a curiosity in the digital world, deepfakes have since become a significant concern, particularly in the context of elections. As the lines between reality and fabrication blur, the potential for deepfakes to influence political discourse and sway voters has grown alarmingly apparent.
Political applications of deepfakes
Deepfakes, or AI-manipulated media, present a complex landscape in political applications, particularly in countries like the United States and India, where the impact can be far-reaching due to their large and diverse populations. Here’s an overview focusing on the positive and negative aspects of deepfakes in the political context of these two nations.
Positive Applications: In the political sphere, deepfake technology has the potential to enhance engagement with voters. Politicians can use deepfakes to create personalised messages, reaching out to supporters in ways that feel direct and intimate. Such technology could also be used to revive past leaders’ speeches, allowing their words to resonate with contemporary audiences, thereby boosting fundraising efforts and rallying support for causes. These applications, while still in their infancy, hint at a future where political communication could be more interactive and engaging, albeit in ways that challenge traditional norms.
Negative Applications: On the flip side, deepfakes have already shown their potential to wreak havoc in the political arena. They can be used to create misleading videos that distort a candidate’s words or actions, potentially altering the course of an election. For instance, a deepfake could falsely depict a political figure making inflammatory remarks, leading to public outrage and a shift in voter sentiment. These negative applications pose a significant threat to democratic processes, as they can be used to spread disinformation, smear opponents, and manipulate public opinion on a massive scale.
Also read: Google reduces deepfake exposure in search results
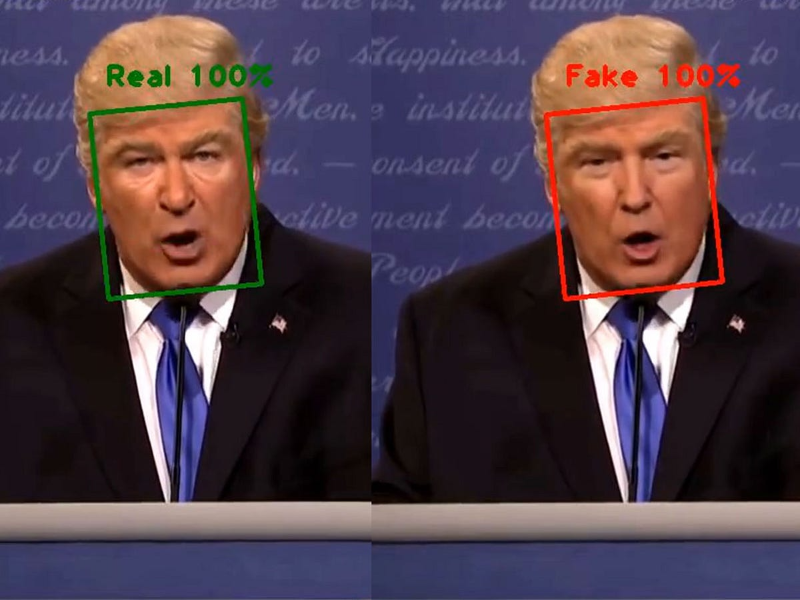

Case studies: United States vs. India
The United States and India present distinctive scenarios when it comes to the impact of deepfake technology in their respective political spheres, making them compelling subjects for comparative analysis.
The U.S. has been at the forefront of technological innovation, including the development of deepfake technology. It has also witnessed attempts to use deepfakes in political campaigns, as well as legislative efforts to combat their malicious use. The Deepfakes Accountability Act of 2019 is a case in point, which underscores the country’s proactive legislative response to the challenges posed by deepfakes. Furthermore, the U.S. has seen instances where deepfake technology was used to create controversial narratives, such as the AI-generated images of political figures in campaign advertisements.
India, with its vast population and burgeoning digital landscape, offers a unique context for the application of deepfake technology. The country has seen deepfakes used in political campaigns, including instances where the digital likenesses of deceased leaders were used for political purposes. The Indian government has shown concern over the potential misuse of AI-generated content and is moving towards establishing a regulatory framework. Additionally, India’s legal system is grappling with the challenges posed by deepfakes, as evidenced by the lack of explicit laws banning them, but with sections of the Information Technology Act 2000 and the Indian Penal Code 1860 being potentially applicable.
The comparison between the U.S. and India highlights the different stages of technological adoption, the diverse applications of deepfake technology in political campaigns, and the distinct regulatory approaches taken by these two nations. While the U.S. has taken legislative action to combat deepfakes, India is in the process of developing a regulatory framework to curb their misuse. The unique cultural, political, and social dynamics in both countries provide a rich ground for analysing the ethical, legal, and societal implications of deepfake technology.
United States: In the United States, deepfake technology has primarily been used to create controversial and misleading content aimed at discrediting political opponents. The 2020 U.S. presidential election saw a surge in deepfake videos, with some targeting prominent candidates to sow confusion and doubt among voters. The highly polarised political environment in the U.S. makes it fertile ground for such manipulative tactics, where deepfakes can quickly go viral, amplifying their impact. The use of deepfakes in the U.S. has sparked debates about the need for stricter regulations and more robust fact-checking mechanisms to protect the integrity of elections.
India: In contrast, India presents a different set of challenges when it comes to deepfakes. With a vast and diverse population, coupled with high levels of digital illiteracy in many regions, deepfakes can spread rapidly, often without the necessary scrutiny to debunk them. During elections, deepfakes have been used to incite communal tensions or discredit political rivals, exploiting existing societal divides. The sheer scale of India’s electorate, combined with the complexity of its political landscape, makes the country particularly vulnerable to the disruptive potential of deepfakes. While both countries face significant risks, India’s unique socio-political environment poses distinct challenges that differ from those in the U.S.
Pop Quiz:
Which statement is true about the impact of deepfakes in elections?
a. Deepfakes are only used for positive political campaigns.
b. Both the US and India have the same challenges with deepfakes.
c. Deepfakes can both engage voters and mislead them.
d. Deepfakes are illegal in all countries.
The correct answer is at the bottom of the article.
Challenges and risks
“The early 2020s will likely be remembered as the beginning of the deepfake era in elections.”
Brennan Centre’s Elections & Government Program
The integration of deepfake technology in political campaigns has introduced a new paradigm of challenges, especially within the electoral landscapes of the United States and India. In the U.S., the rapid advancement of generative AI has been acknowledged with caution by lawmakers, who are grappling with the implications of AI-generated content on the integrity of elections. As noted in a recent analysis by the Brennan Center, “The early 2020s will likely be remembered as the beginning of the deepfake era in elections,” where AI tools can now synthesise audio and video with alarming realism, posing a particular challenge to democracies 131.
In the United States, deepfakes have been a topic of concern due to their potential to disrupt the integrity of elections. The U.S. has seen instances of deepfake technology being used to create controversial narratives, such as the AI-generated images of political figures in campaign advertisements. The country has also taken legislative action to combat deepfakes, with the Deepfakes Accountability Act of 2019 being a significant step towards regulating this technology. However, the rapid advancement of deepfake generation techniques continues to pose challenges for detection and regulation.
India, with its large population and growing digital media consumption, is particularly vulnerable to the impact of deepfakes. The country has witnessed attempts to use deepfake technology in political campaigns, raising concerns about misinformation and manipulation. The Indian government has started to address the issue by considering regulatory measures, although the legal framework is still evolving. The use of deepfakes in India’s elections has the potential to significantly influence public opinion and election outcomes, emphasising the need for effective detection and mitigation strategies.
The challenges and risks associated with deepfakes in both countries include the potential for identity theft, computer fraud, blackmail, and the spread of misinformation. The increasing sophistication of deepfake technology makes it difficult to distinguish between authentic and manipulated content, leading to a rise in cognitive biases such as the “Impostor Bias,” where individuals doubt the authenticity of multimedia due to awareness of AI capabilities. This poses a significant threat to the privacy of personal information and national security, as well as the integrity of democratic processes.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that includes technological, legislative, and educational measures. Developing robust deepfake detection methods, implementing clear regulations, and raising public awareness about the potential misuse of deepfake technology are essential steps in mitigating the risks they pose to elections and society at large.
Regulation and countermeasures
“I’ve already seen demonstrations of deep fake technology that show what looks like me on a screen, saying stuff I did not say. It’s a strange experience people. Without some standards, implications of this technology – for our elections, for our legal system, for our democracy, for rules of evidence, for our entire social order – are frightening and profound.”
Barack Obama, 44th president of the United States
Deepfakes present a complex challenge for democracies, requiring a multifaceted approach to regulation and countermeasures. Here’s an overview of the strategies being considered and implemented to address the impact of deepfakes on political processes, particularly in the context of the U.S. and India.
Insufficiencies in Current Legal Frameworks: Both the U.S. and India are grappling with the inadequacy of current legal frameworks to address the challenges posed by deepfakes. In the U.S., existing laws around defamation and fraud do not fully encompass the unique issues presented by deepfakes. In India, the lack of stringent regulations specifically targeting digital misinformation leaves a significant gap in the legal landscape. This insufficiency highlights the need for updated laws that can more effectively address the creation and dissemination of deepfakes.
International Regulatory Efforts: The global nature of deepfake technology calls for international cooperation in regulatory efforts. While some countries have started to introduce legislation aimed at curbing the use of deepfakes in political campaigns, these efforts remain fragmented. International bodies and agreements could play a crucial role in setting standards and promoting best practices for managing the risks associated with deepfakes, ensuring a more unified approach to this global issue.
Technological Solutions: As the threat of deepfakes grows, so does the development of technology to combat them. Advanced detection tools and algorithms are being created to identify deepfakes by analysing inconsistencies in videos, such as unnatural facial movements or irregularities in lighting and shadows. However, the arms race between deepfake creators and those developing detection tools is ongoing, with each side continually evolving. Despite these efforts, there remains a significant challenge in deploying these tools at scale and ensuring they are accessible to the public, particularly in regions with limited technological resources.
Conclusion
The impact of deepfake technology on politics, particularly in the U.S. and India, underscores the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to mitigate its risks. While deepfakes have the potential to revolutionise political engagement and communication, their misuse threatens the very foundations of democratic systems. As the technology continues to evolve, so too must our legal, ethical, and technological responses. Developing effective regulatory measures, promoting international cooperation, and advancing detection technologies are crucial steps in safeguarding the integrity of elections and ensuring that deepfake technology is used responsibly. The future of democracy in the digital age may well depend on how effectively we rise to this challenge.
The correct answer is C, Deepfakes can both engage voters and mislead them.
