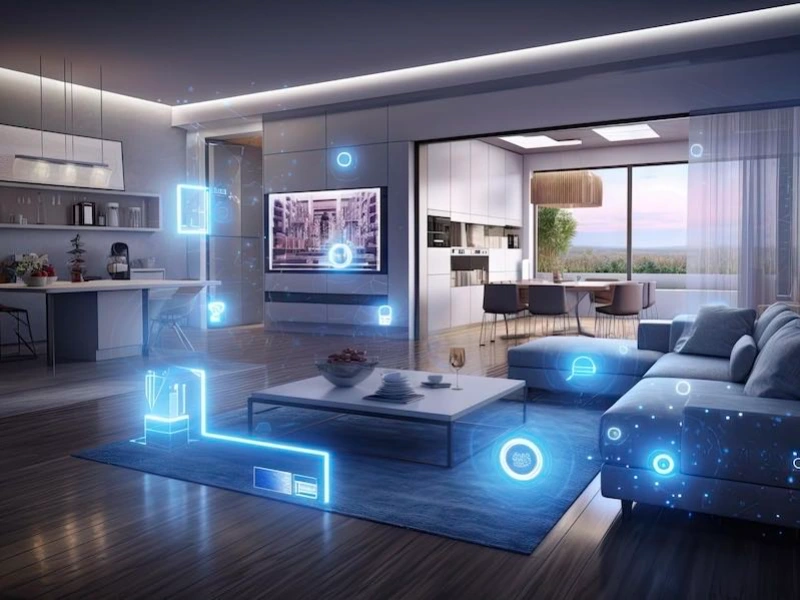
- IoT-driven systems allow remote control of home environments, ensuring laborers return to comfortable living spaces without wasting energy.
- Smart home technologies streamline daily routines by automating lighting, security, and appliance use, reducing the manual effort required after a long day’s work.
- IoT devices provide real-time monitoring and alerts, enhancing the safety of laborers both at home and on the job by ensuring quick responses to potential issues.
In the bustling lives of laborers, balancing work demands and personal life can be a daunting challenge. The advent of smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies is proving to be a game-changer, offering practical solutions to simplify daily tasks, enhance safety, and boost efficiency. Smart home technology refers to interconnected devices within a home that can be controlled remotely, often through a smartphone or voice assistant. IoT extends this connectivity beyond the home, linking various devices and systems to the internet, enabling real-time data exchange and automation.
For laborers, these technologies bring significant benefits. They enable remote management of home environments, ensuring comfort and energy efficiency even after long and exhausting workdays. Automated systems handle routine tasks seamlessly, reducing manual effort and freeing up time for relaxation and family. Furthermore, enhanced safety features offer peace of mind by providing real-time monitoring and alerts, whether at home or on the job. Here are 25 innovative technologies that are transforming the lives of laborers, making their routines easier and more manageable.
Also read: World’s fastest smart car is …
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected devices that exchange data with each other and the cloud. These devices, embedded with sensors and software, range from mechanical and digital machines to everyday consumer objects. IoT enables organisations across various industries to enhance efficiency, improve customer service, make better decisions, and increase business value by allowing data transfer over networks without human intervention.
Examples of IoT devices include a person with a heart monitor implant, a farm animal with a biochip transponder, or a car with sensors to monitor tire pressure. Any object, natural or man-made, that can be assigned an IP address and transfer data over a network can be part of the IoT.
Also read: 12 top IoT integrators: Pioneers in a connected future
Get to know smart home devices
A smart home refers to a convenient home setup where appliances and devices can be automatically controlled remotely from anywhere with an internet connection using a mobile or other networked device. Devices in a smart home are interconnected through the internet, allowing the user to control functions such as security access to the home, temperature, lighting, and a home theater remotely.
A smart home’s devices are connected with each other and can be accessed through one central point—a smartphone, tablet, laptop, or game console. Door locks, televisions, thermostats, home monitors, cameras, lights, and even appliances such as the refrigerator can be controlled through one home automation system. The system is installed on a mobile or other networked device, and the user can create time schedules for certain changes to take effect.
Sure, here is a detailed list of smart home and IoT technologies, with illustrative scenarios demonstrating how each can make life easier for laborers:
1. Smart thermostats
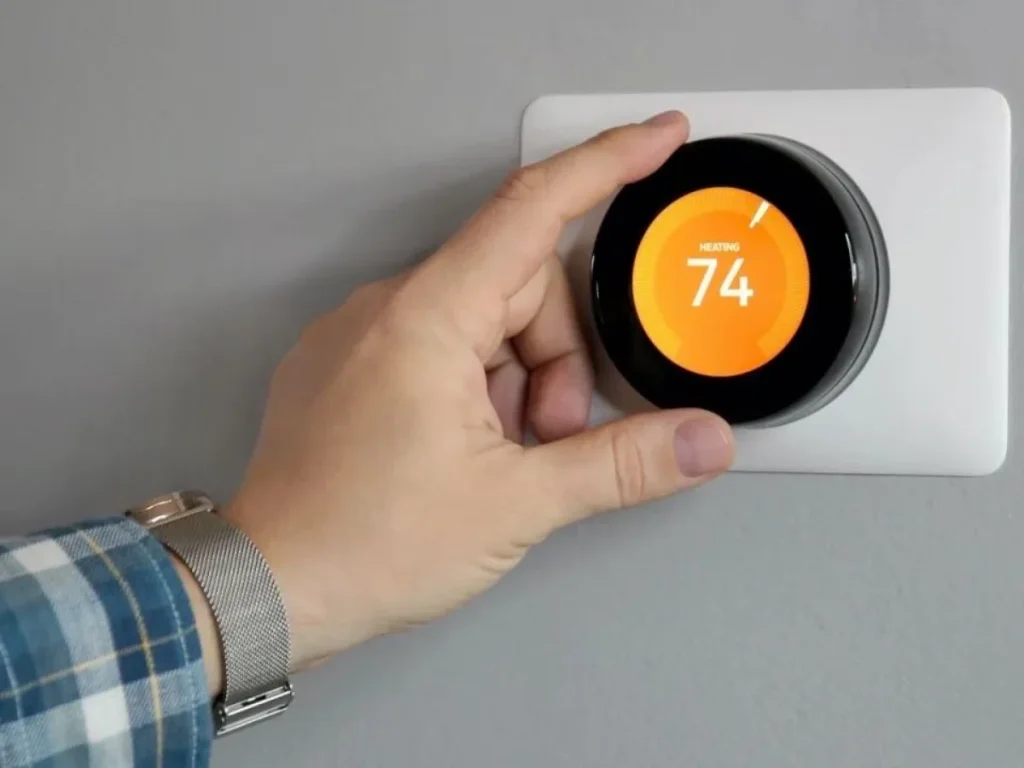

Imagine a construction worker finishing their shift on a sweltering summer day. As they head home, they use their smartphone to adjust their smart thermostat, ensuring their house is refreshingly cool upon arrival. The thermostat learns their schedule over time, automatically setting the perfect temperature to maximise comfort and energy efficiency.
2. Automated lighting system
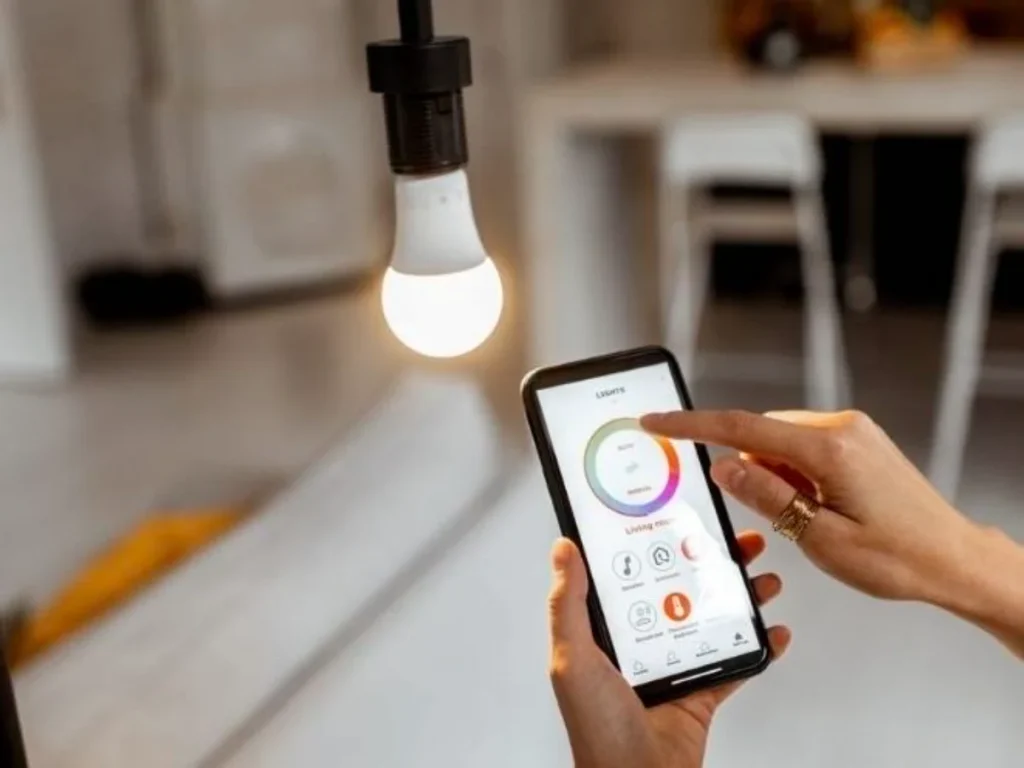

A security guard often returns home late at night. With automated lighting systems, their pathway lights up as they approach the front door, providing a safe and welcoming entry. Inside, the lights adjust to their movement, turning on in occupied rooms and off in empty ones, saving energy and offering convenience.
3. Smart locks
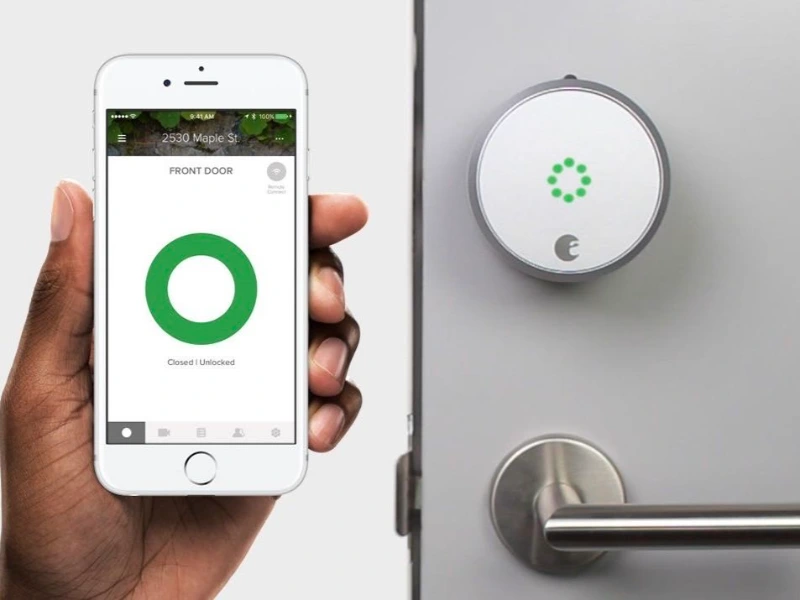

Picture a delivery driver coming home with arms full of packages. Instead of fumbling for keys, they unlock their smart lock with a tap on their smartphone. The smart lock can also provide temporary access codes for trusted visitors, ensuring security without the need for spare keys.
4. Voice-activated assistants

A landscaper finishes a long day and relaxes on their couch. Using a voice-activated assistant like Amazon Alexa, they can control various smart home devices, play music, set reminders for the next day’s tasks, and even order supplies just by speaking.
5. Wearable safety devices
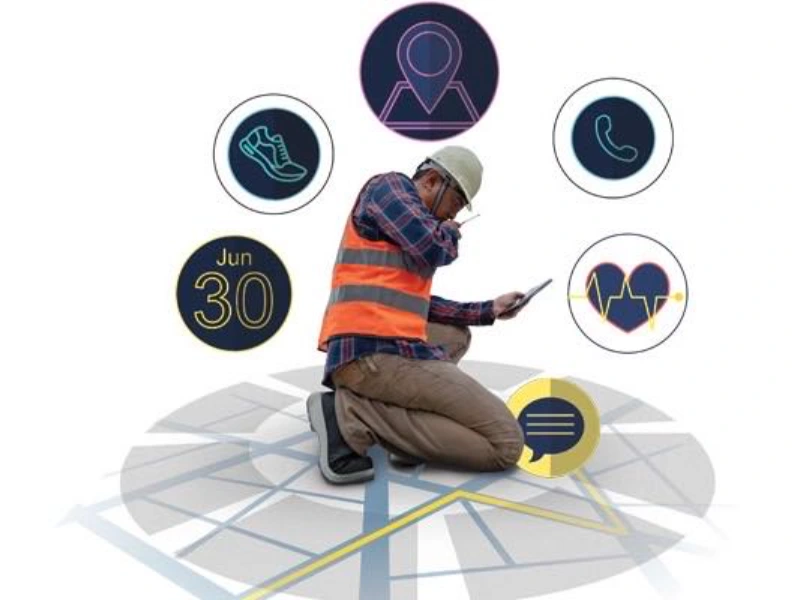

Imagine a miner working deep underground. They wear a safety device that monitors their location and vital signs. In case of an emergency, the device sends an alert to the surface team with the miner’s exact location, ensuring a swift and targeted response.
6. Smart smoke detectors
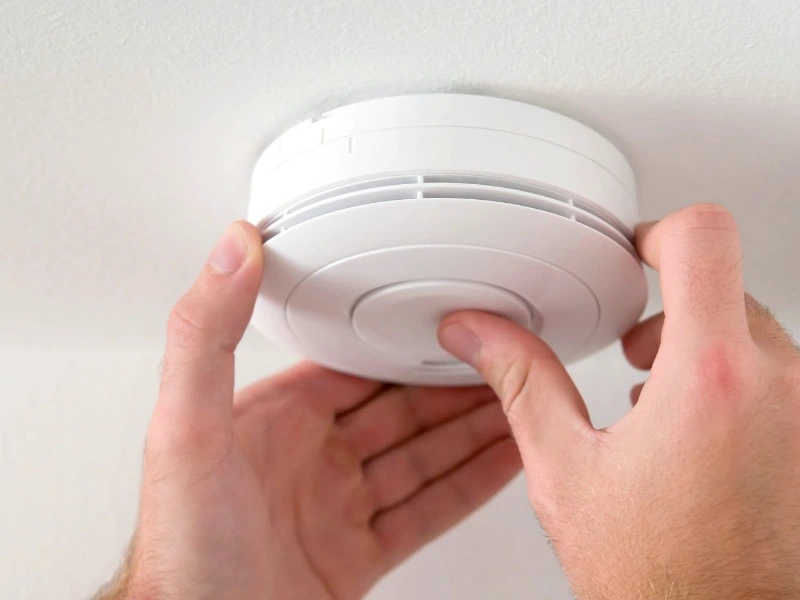

A firefighter’s family is protected by smart smoke detectors that send alerts to their smartphones if smoke is detected, even when they are not at home. This early warning system allows them to act quickly, whether calling emergency services or rushing home to check the situation.
7. Remote monitoring cameras

A truck driver on a long-haul journey uses remote monitoring cameras to check on their home. With live feeds on their smartphone, they can ensure everything is secure and see if packages have been delivered or if family members have arrived safely.
8. Automated irrigation systems
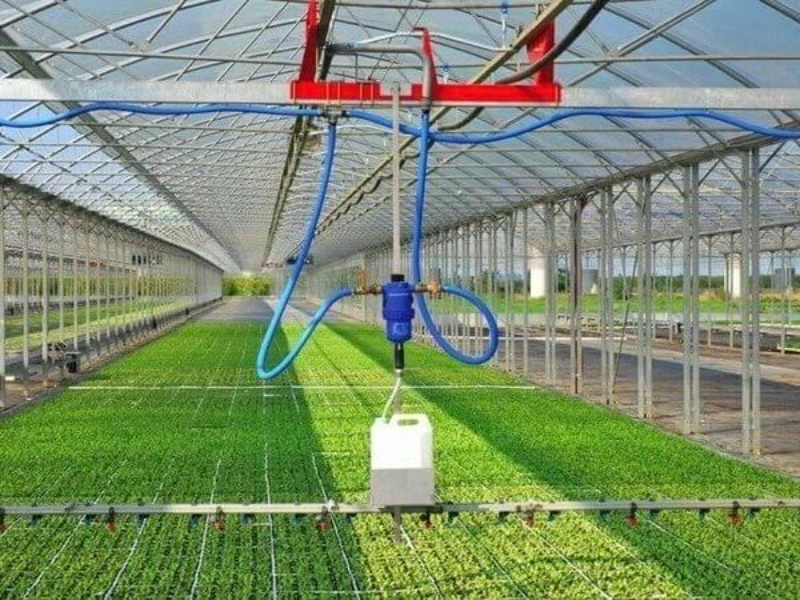

A farmer can optimise water usage on their crops using an automated irrigation system. The system adjusts watering schedules based on real-time weather data, soil moisture levels, and plant needs, ensuring efficient water use and healthy crops with minimal manual intervention.
9. Smart appliances
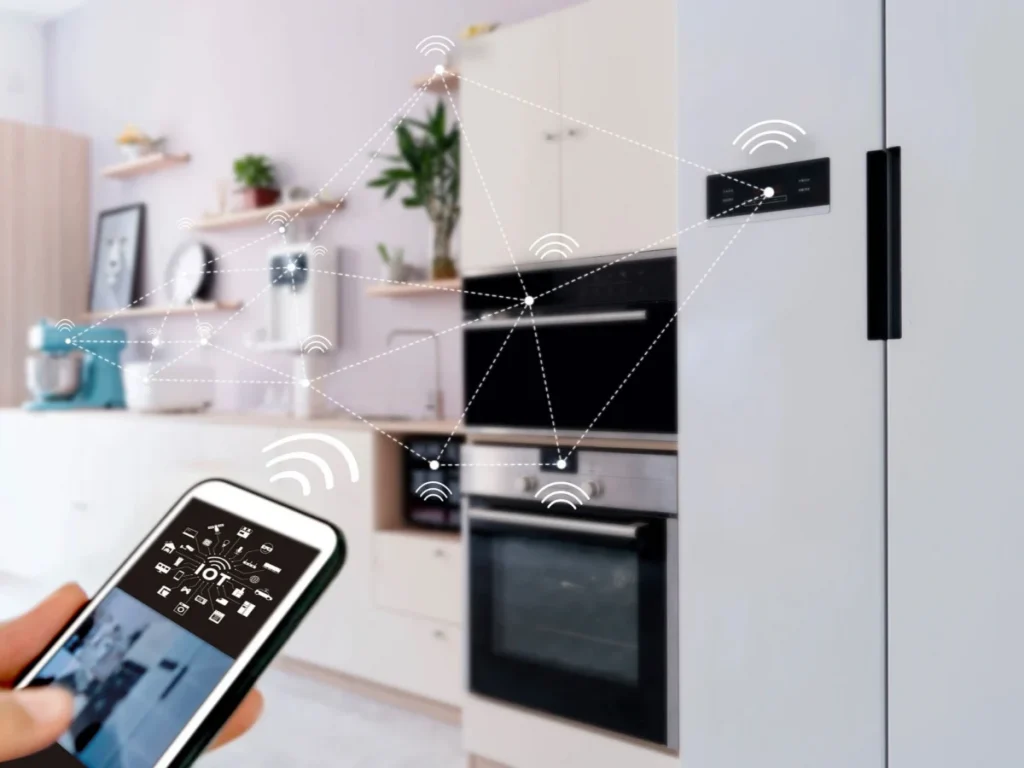

After a busy shift, a chef can check the contents of their smart refrigerator from the grocery store to see what ingredients they need to restock. Smart washing machines can be started remotely, ensuring laundry is done by the time they get home, and ovens can be preheated on their way back.
10. GPS-enabled tools and equipment
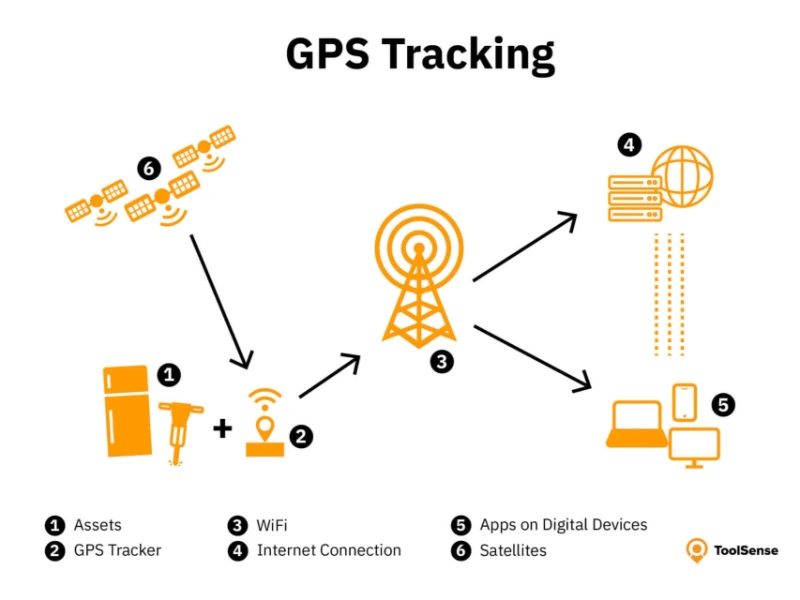
A landscaper can use GPS-enabled tools to track the location of their expensive equipment. If a tool is misplaced or stolen, they can quickly locate it using their smartphone, reducing the risk of loss and improving efficiency on job sites.
11. Smart garage door openers

An electrician with a home garage workshop can use a smart garage door opener to allow deliveries or access for family members without needing to be present. They can open and close the garage door remotely, ensuring tools and equipment are secure when not in use.
12. Energy monitoring systems
An industrial worker can monitor their home’s energy usage in real-time with an energy monitoring system. By identifying high-usage appliances, they can adjust their habits or upgrade to more efficient models, saving money on energy bills without compromising comfort.
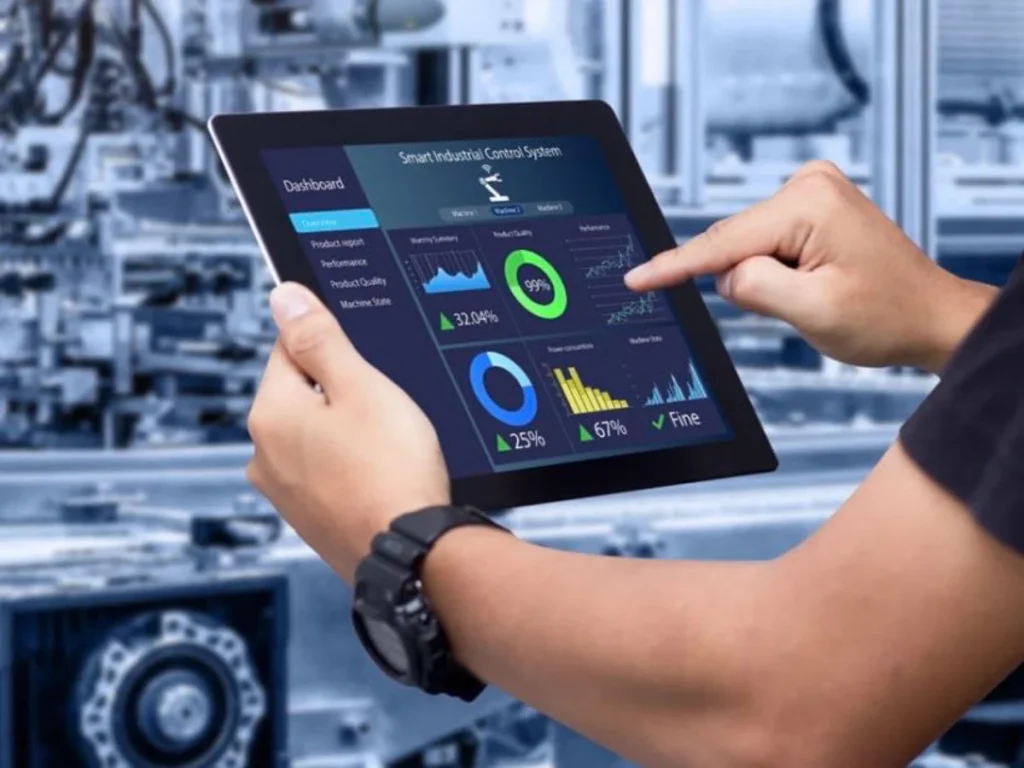

13. Smart home security systems
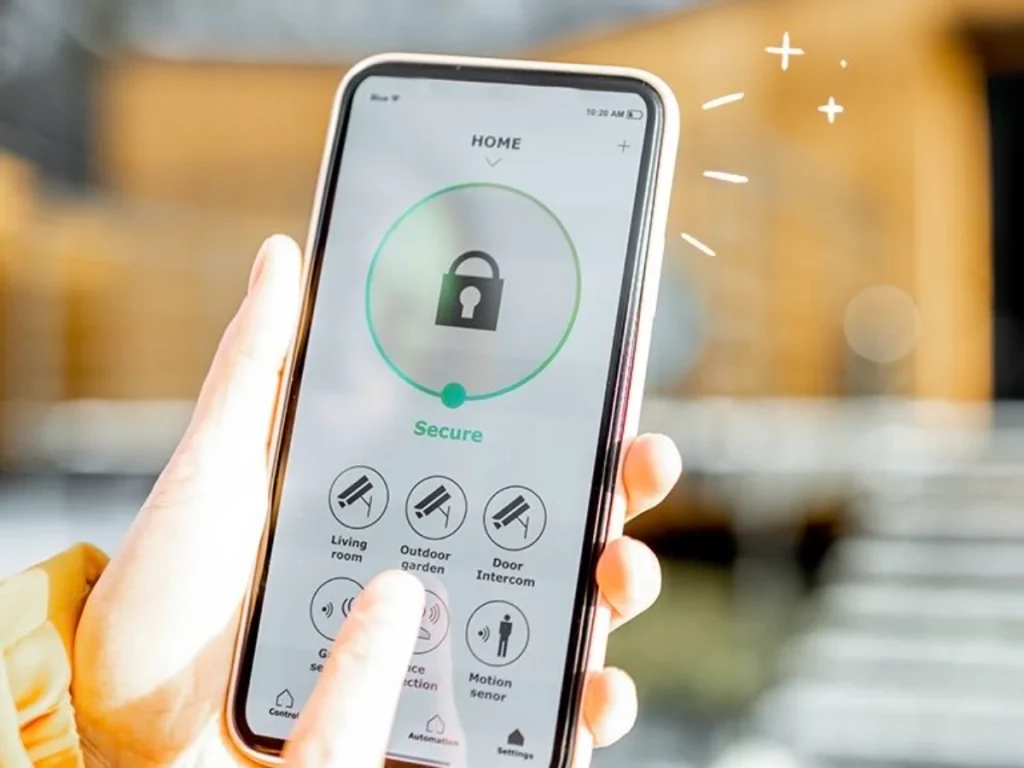

A construction worker can secure their home with an integrated smart security system that includes cameras, sensors, and alarms. They receive real-time alerts on their smartphone if any unusual activity is detected, allowing them to respond quickly, even from a remote job site.
14. Remote vehicle diagnostics

A delivery driver can use remote vehicle diagnostics to monitor the health of their van. The system alerts them to potential issues before they become serious problems, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing the risk of breakdowns on the road.
15. Automated inventory management

A warehouse worker can streamline inventory management with RFID tags and barcode scanners. Automated systems track stock levels and trigger reordering processes, reducing manual counting errors and ensuring they always have the necessary supplies on hand.
16. Smart waste management

A sanitation worker can benefit from smart waste management solutions that optimise collection routes based on real-time data from fill-level sensors in trash bins. This technology reduces unnecessary trips, saves fuel, and improves overall efficiency in waste collection.
17. Personal health monitoring devices
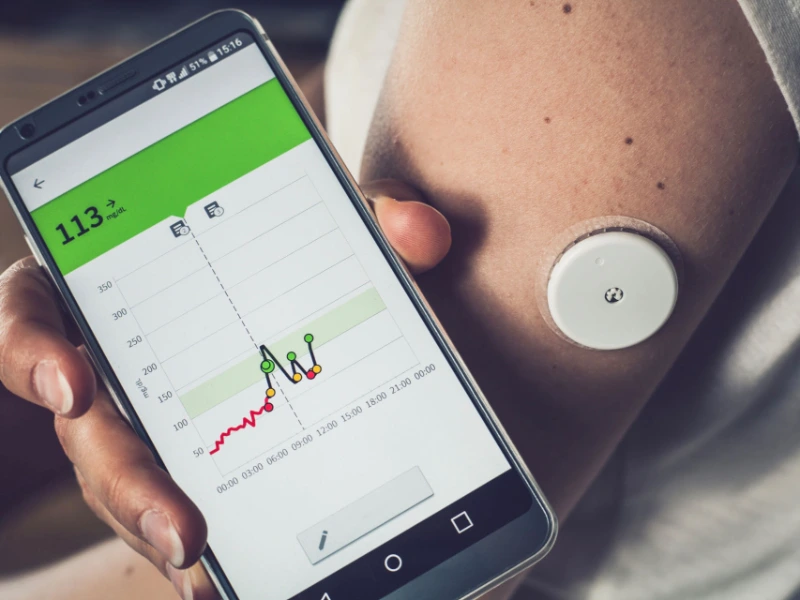

A construction worker can use a fitness tracker to monitor their physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns. By keeping track of their health metrics, they can make informed lifestyle choices to prevent work-related injuries and maintain overall well-being.
18. Smart workwear
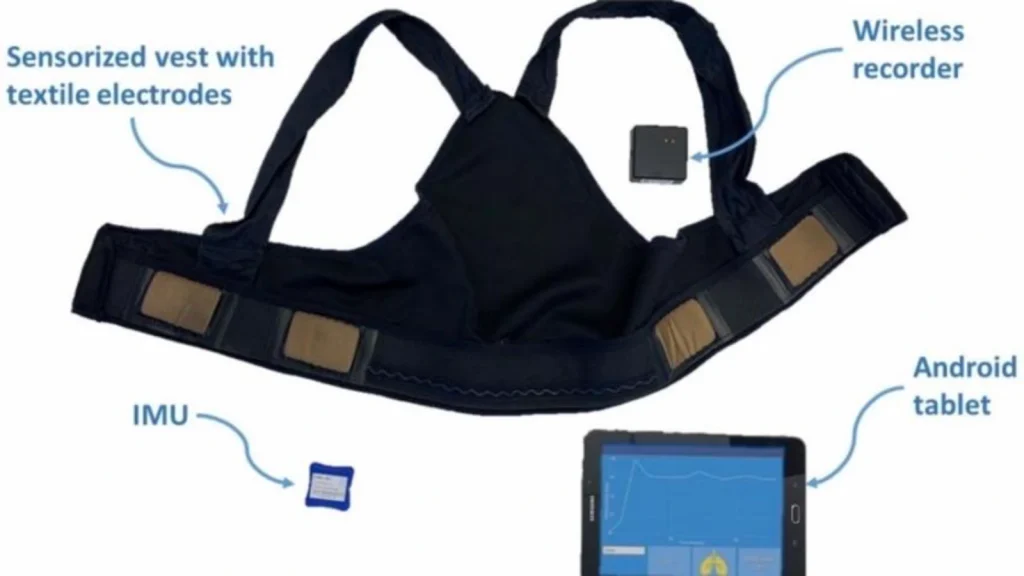

An industrial worker wearing smart workwear embedded with sensors can receive real-time feedback on their posture and movement. This technology can help prevent injuries by alerting them to unsafe movements and ensuring they follow proper ergonomics while lifting or operating machinery.
19. IoT-Enabled fleet management

A logistics manager can track their fleet of delivery trucks in real-time using IoT-enabled fleet management systems. These systems provide insights into vehicle locations, driver behavior, and route efficiency, allowing for optimised deliveries and improved safety.
20. Virtual assistants for administrative tasks

A foreman can use a virtual assistant to automate administrative tasks such as scheduling meetings, organising documents, and setting reminders. This frees up their time to focus on managing the job site and ensuring projects stay on track.
21. Smart farming solutions

A farmer can use IoT sensors and data analytics to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. This information helps them make data-driven decisions on irrigation, fertilisation, and pest control, leading to higher yields and more sustainable farming practices.
22. Remote training and education platforms

A skilled laborer looking to advance their career can use remote training platforms to access online courses and certification programs. This allows them to gain new skills and qualifications without having to take time off work or travel to a training center.
23. Collaborative work management software

A construction project manager can use collaborative work management software to coordinate tasks, share updates, and communicate with their team. This ensures everyone is aligned and informed, reducing misunderstandings and improving project efficiency.
24. Autonomous robotic assistants
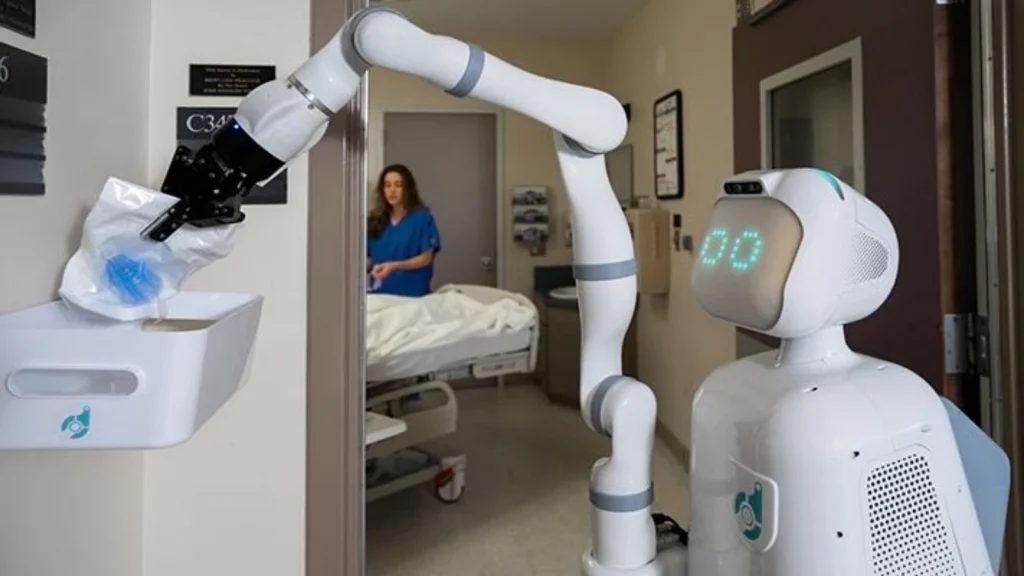

A warehouse worker can rely on autonomous robotic assistants to handle repetitive tasks such as sorting and moving inventory. These robots reduce physical strain on workers, increase productivity, and allow human laborers to focus on more complex and valuable tasks.
25. Predictive maintenance systems
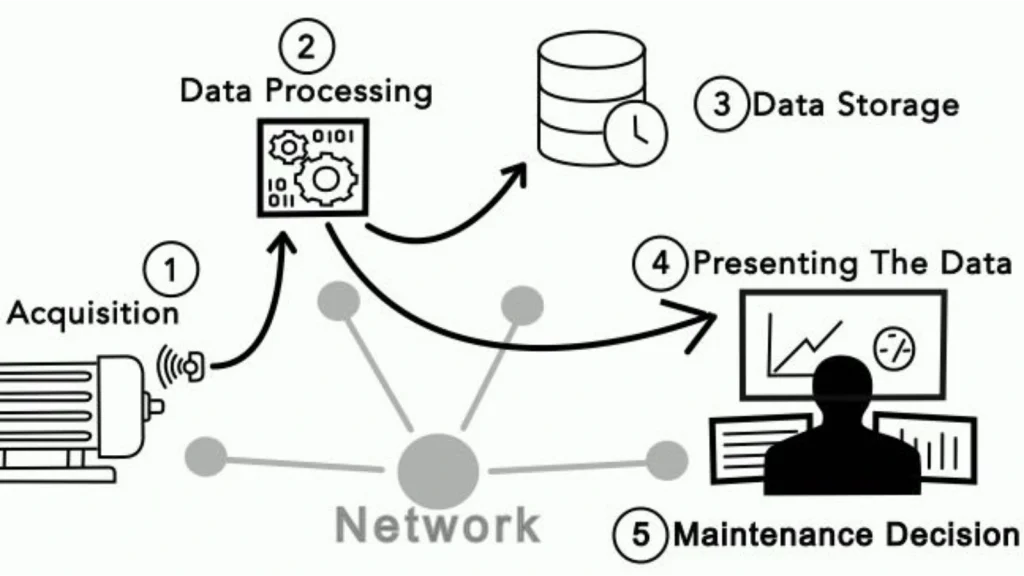
A factory worker can use predictive maintenance systems to monitor machinery health and predict potential failures. By scheduling maintenance proactively based on data insights, they can minimise downtime, extend equipment lifespan, and ensure smooth operations.

