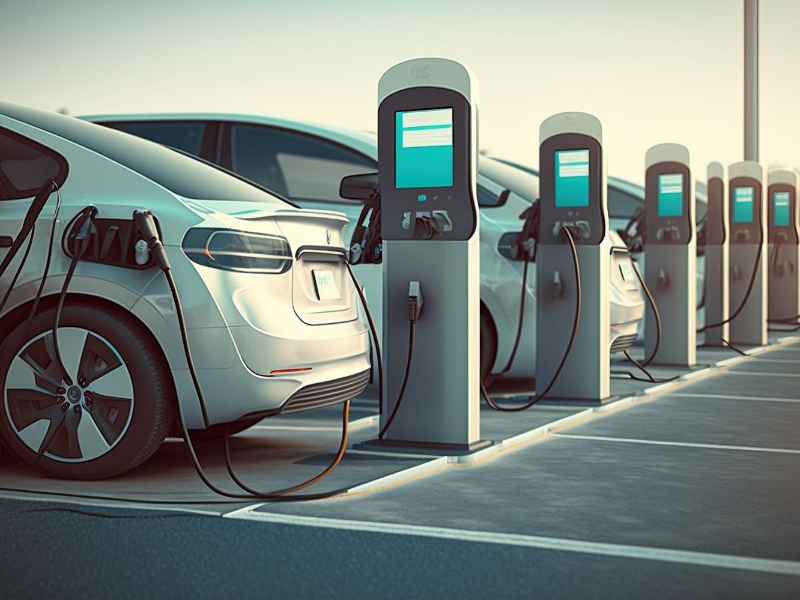
- EV chargers are classified as Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3, each with different charging speeds and power requirements.
- Choosing the Right Chargers involves considering charging speed requirements and usage habits to enhance the EV charging experience.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the way we travel, and understanding the different types of EV chargers is key to making the most of this technology. Whether you’re an EV owner or just curious about the future of transportation, knowing the basics of EV charging will help you navigate the charging landscape with ease.
Charging levels and current types
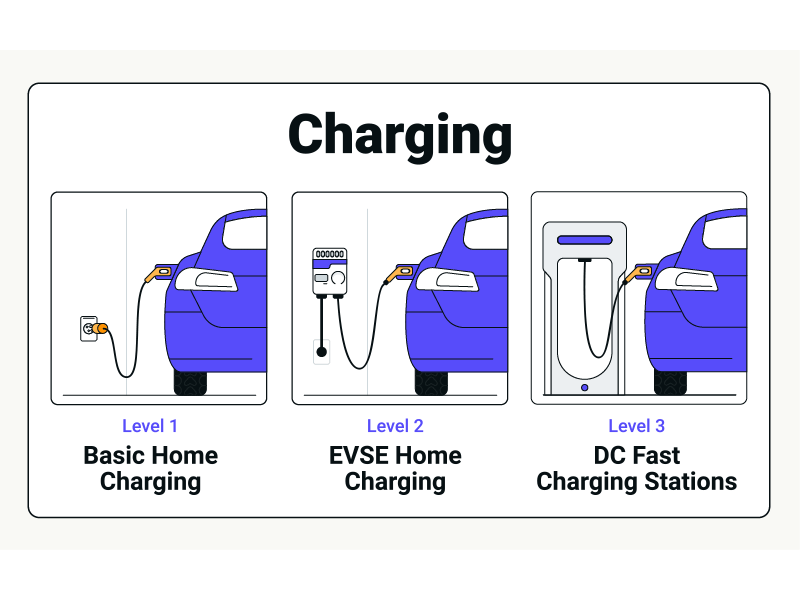
EV charging is categorized into three main levels, each offering a different charging experience:
1. Level 1 (Slow Charging): This is the most basic form of charging, typically found in homes. It uses a standard household electrical outlet and charges an EV at a slow pace, usually overnight. The power output is between 3-6 kW, and it takes 8-12 hours to fully charge an EV.
2. Level 2 (Fast Charging): Level 2 chargers are more powerful and can be found in public spaces like shopping centers, parks, and workplaces. They offer a charging speed of 7kW to 22kW, significantly reducing the time needed to charge an EV. Most EVs and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are compatible with Level 2 chargers.
3. Level 3 (Rapid Charging): This is the fastest charging option, using direct current (DC) to charge an EV. Level 3 chargers can charge an EV up to 80% in about 20 minutes and provide a full charge in around an hour. They are typically found at motorway service stations and are ideal for long-distance travel.
AC and DC chargers: A closer look
- AC Chargers (Level 1 and Level 2): AC chargers convert the incoming AC current to DC at the vehicle’s onboard charger. They are suitable for home and public charging, with a maximum power of 7kW for domestic supply. Key features include compatibility with various AC connectors and the option for tethered or untethered cables.
- DC Charger (Level 3): DC chargers are the fastest, converting AC to DC at the charging station. They come in single or double-gun variants, capable of charging one or two EVs simultaneously. Power outputs range from 50 kW for rapid charging to over 100 kW for ultra-rapid charging.
Key features of each charger type
An EV charger is a device that pulls electrical current from a power source and delivers it to an EV, ensuring the battery remains charged.
1. Level 1 Chargers: Ideal for home use, these chargers offer convenience and flexibility. They are user-friendly, often equipped with multiple AC connector types, allowing for tethered or untethered charging options.
2. Level 2 Chargers: Known for their versatility, Level 2 chargers can offer different charging speeds depending on the EV model and connector type. They are suitable for a wide range of EVs, making them a popular choice for public charging stations.
3. Level 3 Chargers: Designed for high-speed charging, these chargers are equipped with tethered cables for safety and efficiency. They can provide power outputs of 50 kW for rapid charging or over 100 kW for ultra-rapid charging, significantly reducing waiting times for long-distance travel.
Also read: 7 top players in EV charging world
EV charger connector types
Different connectors support different charging rates, and compatibility is crucial.
Here are the main types:
- Type 1: Used primarily on older models and Asian-built EVs, supporting charging rates from 3kW to 7kW.
- Type 2: The most common connector in the UK, supporting rates from 3kW to 43kW.
- CHAdeMO: A rapid charging connector, supporting rates from 25kW to 100kW, originally developed by Japanese manufacturers.
- CCS: Another rapid charging connector, supporting rates from 50kW to 350kW, developed by German manufacturers.

Charging time and compatibility
The time it takes to charge an EV varies greatly depending on the charger type. From the leisurely pace of a standard socket to the lightning-fast ultra-rapid chargers, drivers need to plan their charging strategy accordingly. It’s important to note that the actual charging time can also be influenced by factors such as the battery’s state of charge and the charger’s current availability.
Compatibility is a critical factor when choosing an EV and its charging solutions. Each EV model has a maximum charge rate, which determines how quickly it can be charged. For example, an older Nissan Leaf has a maximum charge rate of 6.6kW, meaning it will not benefit from a higher power charger. Understanding these limitations is essential for avoiding disappointment during long trips.
Also read: DFI launches multipurpose EV charging platform
Additional tips
- Always check the compatibility of chargers and connectors with the EV model before setting off on a journey.
- Plan routes to include charging points to avoid any potential delays during long trips.
- Keep an eye on advancements in EV technology, as they can significantly impact charging times and capabilities.
By grasping the fundamentals of EV charging, one can fully leverage the benefits of an electric vehicle and enjoy cleaner, more sustainable transportation.

