- NLB is a feature embedded within operating systems to evenly distribute network traffic across multiple servers or virtual machines.
- Network Load Balancing stands as an integral element of modern IT infrastructures, ensuring the efficient management of traffic and the steadfast availability of services.
In the realm of technology, maintaining seamless network operations is paramount. One pivotal technique that aids in this endeavour is Network Load Balancing (NLB). This piece aims to elucidate NLB, delineating its function, mechanism, and the myriad advantages it confers upon contemporary IT infrastructures.
Grasping NLB
NLB is a feature embedded within an array of operating systems, such as the Microsoft Windows Server, and cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS). It is engineered to evenly disseminate network traffic across a constellation of servers or virtual machines (VMs) within a cluster. This equitable distribution averts the risk of any single host becoming overwhelmed, thereby bolstering the network’s overall efficacy.
Operational insight into NLB
NLB functions by establishing TCP connections with chosen targets, such as servers or instances, and scattering the processing burdens and network traffic. Within the Windows ecosystem, it can orchestrate multiple servers as a unified virtual cluster. AWS’s NLB, in its turn, apportions incoming traffic across a multitude of targets, exemplified by Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud instances.
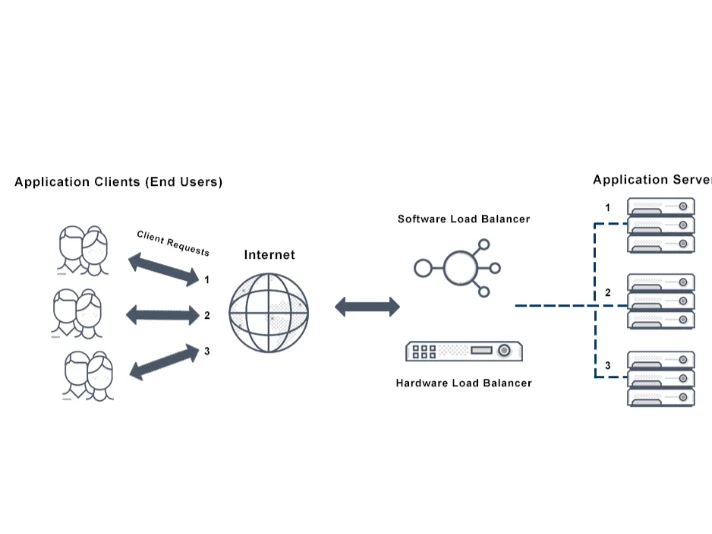
NLB’s utility
NLB is especially advantageous for stateless applications, such as web servers utilising Internet Information Services. By directing traffic to available hosts without interruption, NLB ensures these services remain robustly accessible with minimal downtime. It also finds application in File Transfer Protocol servers, proxy servers, firewall servers, and virtual private networks.
NLB within the OSI layers
NLB is operational at both the transport layer (Layer 4) and the application layer (Layer 7) of the OSI model. At Layer 4, it employs straightforward algorithms like round-robin routing for proficient packet-level load balancing. At Layer 7, NLB examines the substance of each message, facilitating more nuanced routing decisions and supporting intelligent routing and efficient traffic distribution.
Also read: What is Network as a Service (NaaS) in cloud computing?
NLB implementation in Windows server
Versions of Windows server, including 2022, 2019, and 2016, offer NLB capabilities. It amalgamates multiple computers into a cohesive virtual cluster, with each host operating its own server OS. Administrators can tailor NLB to apportion client requests in accordance with their specifications and Microsoft’s proprietary distribution algorithm.
NLB management in AWS
AWS Elastic Load Balancing supports NLB in conjunction with other load balancer types. The AWS NLB comprises a listener and a target group, which identify client requests and transmit them to registered targets via various protocols. It can distribute traffic across availability zones and facilitates cross-zone load balancing when activated.
Also read: Navigating the hybrid cloud: Maximising flexibility and security
The merits of NLB
The benefits of NLB are manifold. It enhances application availability, delivery, performance, and scalability. Should a host falter, NLB promptly redistributes the load amongst other hosts, curtailing downtime. It also permits the facile augmentation or reduction of services and supports maintenance activities without disrupting the network.
Network Load Balancing stands as an integral element of modern IT infrastructures, ensuring the efficient management of traffic and the steadfast availability of services. By comprehending and deploying NLB, organisations can augment their network performance and reliability.

