- Cloud computing is a mode of providing computing resources and services to users via the internet. NaaS is an integral part of the cloud computing ecosystem, providing networking capabilities that complement the computing, storage, and application services offered by other cloud models.
- NaaS providers offer a variety of services to help organisations manage and optimise their network infrastructure, including Amazon Web Services Virtual Private Cloud, Microsoft Azure Virtual Cloud and Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud.
- NaaS is often used alongside other terms within the realm of cloud computing such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Software-Defined Networking (SDN).
Network as a Service (NaaS) stands for a business model where networking services are provided to customers over the internet. It is an integral part of the cloud computing ecosystem, providing networking capabilities that complement the computing, storage, and application services offered by other cloud models.
The rise of cloud computing
The concept of “cloud” traces back to 1994 when General Magic used it to describe the virtualised environment for mobile agents in the Telescript system. David Hoffman, a communications specialist at General Magic, is credited with coining the term based on its existing usage in networking and telecom.
The “cloud” essentially functions as a network. Narrowly speaking, cloud computing is a type of network that provides resources, allowing users to access resources from the “cloud” whenever needed, on a pay-as-you-go basis. It’s akin to an endless expansion, much like how we access water from a utility company, paying based on our actual usage, without any limitations.
Cloud computing is a mode of providing computing resources and services to users via the internet. In cloud computing, computing resources such as servers, storage devices, and applications are consolidated into a virtual resource pool that users can access and use on demand. Cloud computing provides a high degree of scalability and flexibility, allowing users to perform large-scale calculations and data processing without having a powerful computing infrastructure on-premises.
Also read: Cloud connection: Bridging today’s needs with tomorrow’s innovations
NaaS is an integral part of the cloud computing ecosystem, providing networking capabilities that complement the computing, storage, and application services offered by other cloud models.
This integration enhances the overall efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of IT operations for business and can offer several benefits, such as reduced capital expenditure, increased flexibility, scalability, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing networking needs.
What is NaaS?
Network as a Service (NaaS) stands for a business model where networking services are provided to customers over the internet. Instead of companies owning, managing, and maintaining their networking infrastructure, they can leverage NaaS providers to access networking resources on a subscription or pay-per-use basis.
NaaS also involves the optimisation of resource allocations by considering network and computing resources as a unified whole. To put it simply, NaaS can encompass various networking functions, including virtual private networks (VPNs), bandwidth on demand, content delivery networks (CDNs), and more, providing a comprehensive solution for modern networking needs.
NaaS has many key features different from other services. It is a kind of on-demand Networking that customers can quickly provision and scale networking services as needed without significant upfront investment. NaaS providers can handle the management, maintenance, and security of the networking infrastructure.
By paying only for the networking resources used, companies can better manage their expenses and avoid over-provisioning. NaaS also allows businesses to easily adjust their networking capabilities to match their changing requirements.
NaaS providers offer a variety of services to help organisations manage and optimise their network infrastructure, enhance security, and achieve greater flexibility and scalability in their network operations.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) offers NaaS solutions that allow users to create isolated network environments within the AWS cloud, with control over IP addressing, subnets, and routing.
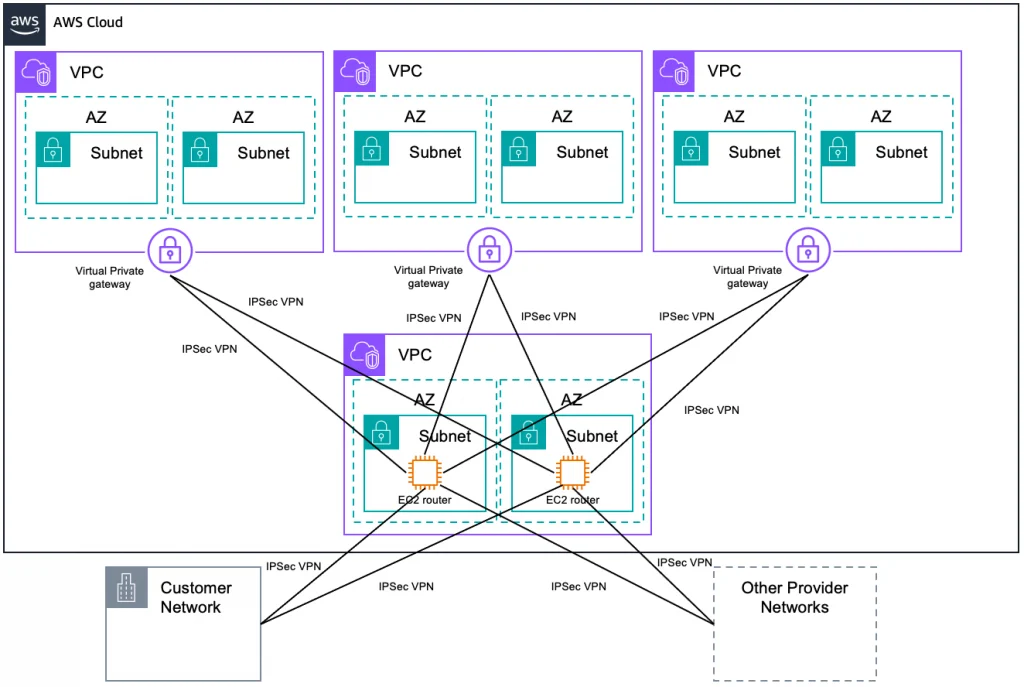
Microsoft Azure provides virtual networking services, including VPN gateways, load balancers, and application gateways, enabling users to build and manage their cloud-based network infrastructure.
Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) offers a range of networking services, such as VPCs, interconnects, and global load balancing, to help users create scalable and secure network architectures.
Related services of NaaS
NaaS is often used alongside other terms within the realm of cloud computing such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Software-Defined Networking (SDN).
IaaS is a form of cloud computing that provides virtualised computing resources over the internet. IaaS offers businesses the ability to rent infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking hardware, on a pay-as-you-go basis, eliminating the need to invest in and maintain physical hardware.
Also read: Artificial intelligence infrastructure, the backbone of AI application and advancement
PaaS is also a cloud computing model that provides developers with a platform to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS offers a range of services and tools that simplify the development process, enabling developers to focus on writing code and creating applications.
SaaS stands for another cloud computing model where software applications are delivered over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access the software through a web browser, without the need to install, maintain, or manage any underlying hardware or software infrastructure.
SDN stands for Software-Defined Networking. It is an approach to networking that uses software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) to communicate with underlying hardware infrastructure and direct traffic on a network. This allows for more flexible and efficient network management compared to traditional hardware-based networking.

