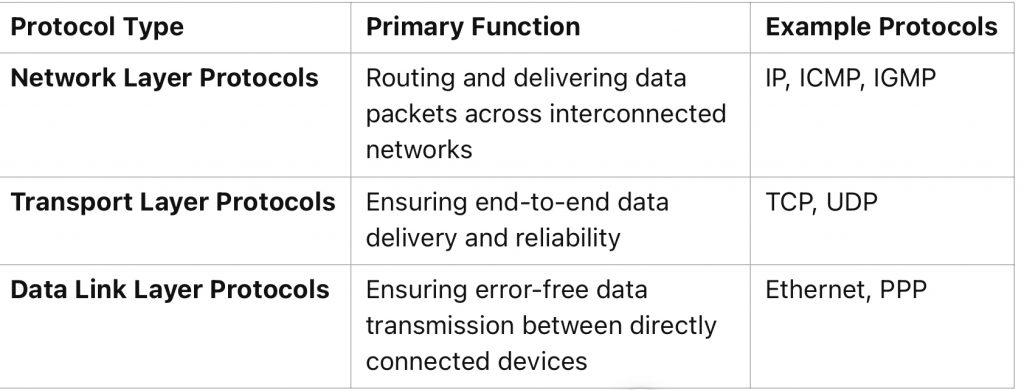
- Network layer protocols manage addressing, routing, and delivering data across interconnected networks, ensuring efficient communication.
- Common protocols include IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
- The evolution of protocols, such as the transition to IPv6 and AI-optimised routing, is shaping the future of scalable and secure digital communication.
A network layer protocol is a set of rules that governs the transmission of data packets across networks. As part of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, the network layer plays a pivotal role in routing, addressing, and delivering data from one device to another across interconnected networks. Common examples of network layer protocols include IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
By ensuring that data packets reach their correct destination, the network layer protocol enables seamless communication across devices, even when they belong to different networks. Without this critical layer, modern networking as we know it would not be possible.
Also read: Network layer protocol enables efficient data transmission
Also read: What are the layers and layered models of network protocols?
- How the network layer works
- Common network layer protocols
- The role of network layer protocols in modern communications
- Key features of network layer protocols
- Differences between network layer protocols and other protocols
- Applications of network layer protocols
- Challenges facing network layer protocols
- Advancements in network layer protocols
- Learning more about network layer protocols
- The backbone of modern networking
- FAQs: Network layer protocols
How the network layer works
The network layer is the third layer in the OSI model, sitting above the data link layer and below the transport layer. Its primary function is to handle packet routing—determining the best path for data to travel across multiple networks. As Eric Schmidt, former CEO of Google, said “The Internet is the first thing that humanity has built that humanity doesn’t understand, the largest experiment in anarchy that we have ever had.”
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how the network layer functions:
Logical addressing: The network layer assigns unique IP addresses to devices. This addressing ensures that data packets are sent to the right destination.
Routing: Based on the destination IP address, the network layer determines the optimal path for data to travel, even across different networks.

Fragmentation: If a data packet is too large for the transmission medium, the network layer splits it into smaller fragments for easier transport.
Error handling and diagnostics: Protocols like ICMP help diagnose and correct transmission errors.
The Internet is the first thing that humanity has built that humanity doesn’t understand, the largest experiment in anarchy that we have ever had
former CEO of Google
Common network layer protocols
Internet Protocol (IP): The Internet Protocol (IP) is the most widely used network layer protocol. It handles addressing and routing, ensuring data packets reach their correct destination. IP operates in two versions:
• IPv4: The older version, supporting about 4.3 billion unique addresses.
• IPv6: Introduced to handle the growing number of devices, IPv6 offers an almost unlimited address space and improved security features.
Also read: What are different types of common network protocols used for?
Also read: What is IPv6 and what are its features?

Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP): ICMP is used for error reporting and network diagnostics. For instance, tools like Ping and Traceroute rely on ICMP to test network connectivity and identify bottlenecks.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP): IGMP manages multicast group memberships, enabling devices to receive broadcast messages efficiently. This is particularly useful for applications like streaming or online conferencing.
Also read: What do network protocols do?
Also read: What does protocol mean in networking?
The role of network layer protocols in modern communications
Network layer protocols are integral to digital connectivity. They handle data transmission across diverse networks, including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and the internet. As John Gage, co-founder of Sun Microsystems, said “The network is the computer.” Their key roles include:
Facilitating interconnectivity: They allow devices from different manufacturers or running different operating systems to communicate seamlessly.
Optimising network performance: By selecting efficient routes, network layer protocols minimise latency and improve overall speed.
Enabling scalability: They support the growing number of devices in a network, ensuring reliable performance even under high traffic.

Enhancing security: Protocols like IPv6 incorporate features that safeguard data against interception or tampering.
Also read: The key role of network protocols in modern communications
Also read: What is the most widely used local area network protocol?
The network is the computer
John Gage, co-founder of Sun Microsystems
Key features of network layer protocols
Logical addressing: Unlike physical (MAC) addresses, logical addresses (IP addresses) are unique to each device and essential for communication across interconnected networks.
Routing: Routing is the process of selecting the best path for data packets to travel. Protocols like RIP (Routing Information Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) play a crucial role in this.
Quality of Service (QoS): QoS ensures prioritisation of specific types of network traffic, such as video calls or online gaming, to maintain consistent performance.
Error Reporting and Diagnostics: ICMP assists in identifying and resolving issues like packet loss or unreachable destinations.
Differences between network layer protocols and other protocols
While network layer protocols focus on addressing, routing, and delivering data packets across networks, other protocols serve different purposes.
Applications of network layer protocols
Network layer protocols are ubiquitous, powering a wide range of applications.
Internet browsing: When you access a website, the IP protocol ensures your request reaches the correct server, and the server’s response returns to your device.
Video streaming: Streaming platforms like Netflix rely on network layer protocols to deliver high-quality video to millions of users worldwide. Multicast protocols like IGMP are used to optimise bandwidth usage.
IoT devices: Smart home devices use IPv6 to connect to the internet and communicate with other devices, ensuring seamless automation.

Online gaming: In online multiplayer games, network layer protocols facilitate low-latency communication between players, ensuring a smooth gaming experience.
Challenges facing network layer protocols
Scalability: The explosive growth of connected devices has pushed IPv4 to its limits. Transitioning to IPv6 is critical but challenging due to legacy systems.
Security vulnerabilities: Network layer protocols are often targeted by attackers. For example, IP spoofing can be used to mask malicious activities. Protocols must continually evolve to address such threats.
Fragmentation issues: Fragmenting large data packets can lead to inefficiencies. Protocols must balance fragmentation with network performance.
Compatibility concerns: Integrating newer protocols with legacy systems can be complex and resource-intensive.
Advancements in network layer protocols
With the advent of 5G, AI, and blockchain, network layer protocols are evolving rapidly:
AI-Optimised routing: AI is being integrated into routing protocols to dynamically optimise network traffic and improve efficiency.
Decentralised protocols: Blockchain is inspiring decentralised network protocols, offering enhanced transparency and security.

Support for 5G networks: Protocols are being adapted to meet the demands of 5G, including higher speeds, reduced latency, and increased device densities.
IPv6 adoption: Organisations are transitioning to IPv6 to handle the growing number of internet-connected devices and improve security features.
Learning more about network layer protocols
Explore networking courses: Online platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer courses on networking fundamentals. Certifications such as Cisco CCNA and CompTIA Network+ provide industry-recognised credentials.
Practice with tools: Tools like Wireshark allow users to capture and analyse network traffic, providing hands-on experience with network layer protocols.
Stay updated: Follow tech blogs, research papers, and industry news to keep up with advancements in networking.
The backbone of modern networking
Network layer protocols are the backbone of modern communication, enabling data to traverse complex networks seamlessly. From assigning logical addresses to determining the best routes for data packets, these protocols ensure efficiency, reliability, and scalability. As technology advances, the evolution of network layer protocols will remain pivotal in shaping the future of digital communication.
By understanding how these protocols work and their real-world applications, IT professionals and tech enthusiasts can better navigate the ever-expanding world of networking.
FAQs: Network layer protocols
Network layer protocols are responsible for routing, addressing, and delivering data packets across interconnected networks, ensuring efficient and reliable communication.
Common examples include Internet Protocol (IP), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), and Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP). These protocols handle tasks like addressing, error reporting, and multicast management.
IP assigns unique addresses to devices and determines the best route for data packets to travel across networks. It has two versions: IPv4, with limited address space, and IPv6, which offers a larger address pool and better security.
They facilitate seamless connectivity across devices, optimise network performance, and enable scalability by managing large volumes of data traffic. They are essential for applications like internet browsing, video streaming, and IoT communication.
IPv6 is critical because it addresses the limitations of IPv4, such as its limited address space. With a virtually unlimited address capacity and enhanced security features, IPv6 supports the growing number of internet-connected devices and future networking demands.

