- Essential elements include a detailed asset inventory, risk assessment, and clear RTO and RPO objectives for efficient data recovery.
- A robust plan also encompasses effective communication strategies, partner and vendor coordination, comprehensive backup solutions, defined roles, and regular testing to maintain business resilience.
In the digital landscape, businesses are vulnerable to a myriad of threats that can lead to severe data loss and operational disruptions. A robust disaster recovery plan is indispensable for ensuring continuity and resilience. Despite the majority of IT decision-makers claiming to have a plan, the reality is that many lack the depth and maturity needed for true preparedness. This article breaks down the eight essential elements of an effective disaster recovery plan, providing a clear framework for businesses to safeguard their operations.
1. Inventory all assets
Start by meticulously cataloging every IT asset, from hardware and software to data and network resources. Ranking these assets according to their business criticality forms the foundation for a comprehensive risk assessment.
Also read: What is cloud backup and recovery?
2. Execute a comprehensive risk assessment
Identify the threats your business faces through a detailed risk assessment. This involves:
- Evaluating the importance of critical assets for recovery prioritisation.
- Identifying potential threats and assessing their impact.
- Prioritising threats based on likelihood and potential damage.
- Reviewing existing security measures and disaster recovery strategies for effectiveness.
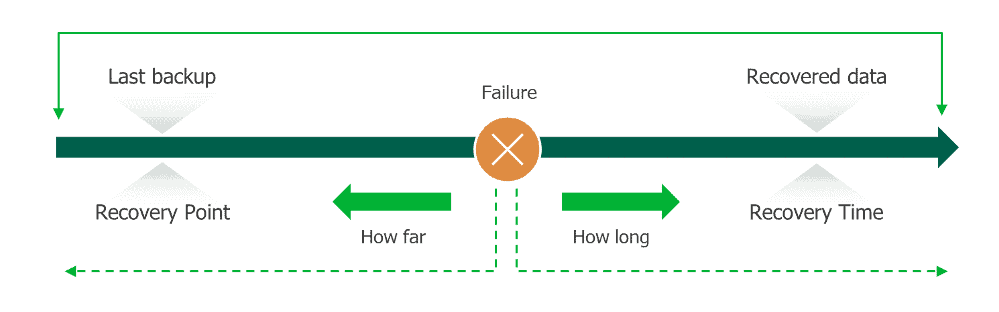
3. Establish clear recovery objectives
Set Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPOs) to guide your disaster recovery strategy. Consider the following when defining these objectives:
- Conduct a business impact analysis to understand the operational, financial, and reputational impacts of downtime.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and legal requirements.
- Evaluate the interdependencies of business processes and IT systems.
- Assess the operational capabilities and resources needed to meet your RTO.
4. Build an effective communication plan
Communication is key in a crisis. Develop a plan that includes:
- Designating a crisis communications team with trained individuals and a spokesperson.
- Establishing communication objectives and strategies for various stakeholders.
- Identifying internal and external stakeholders and tailoring communication strategies.
- Setting up communication channels and creating predefined messages for different scenarios.
- Assembling and regularly updating comprehensive contact lists.
5. Establish guidelines for partner and vendor coordination
Prepare to coordinate with external entities during a disaster. This includes:
- Identifying critical vendors and partners essential to operations.
- Defining their roles and responsibilities within your disaster recovery plan.
- Reviewing contracts to understand obligations and service-level agreements.
6. Implement a comprehensive backup strategy
Adopt a failsafe approach to data backups with the 3-2-1-1 strategy, ensuring multiple copies of data are stored in separate locations and at least one version is immutable.
Also read: Cloud data protection: Definition, benefits and methods
7. Define roles and responsibilities
Clarify the roles and responsibilities of the crisis communications team, disaster recovery team, and other key personnel. Regular training and drills are crucial to maintain readiness and clarity of roles.
8. Test and update your plan regularly
Regular testing and updates are vital to ensure the plan’s effectiveness. Simulation of various scenarios followed by evaluations and plan revisions will keep your disaster recovery plan current and relevant.
A disaster recovery plan is more than a document; it’s a strategic tool for business survival. By incorporating these eight elements, businesses can create a resilient framework that not only prepares them for the unexpected but also positions them to recover stronger. The aim is to minimise disruption and ensure a swift return to normal operations.

