- Ethernet cables are the lifelines of modern networking, enabling data transmission across devices.
- An ethernet cable is a type of networking cable used to connect devices to a local area network (LAN) or to the internet.
Ethernet cables remain a staple in networking due to their reliability, speed, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding how they work and their role in data transmission is essential for anyone looking to set up or improve a network infrastructure. This blog will explain what ethernet cables are, how ethernet cables work, and their advantages and disadvantages.
What is an ethernet cable
Ethernet, a foundational Internet technology, enables the interconnection of various devices within a unified network. An ethernet cable, serving as the physical link, is an insulated bundle of wires housed within a protective sheath. One end of this cable typically connects to a modem or router, while the other end is plugged into the device in use, such as a computer, establishing a reliable network connection.
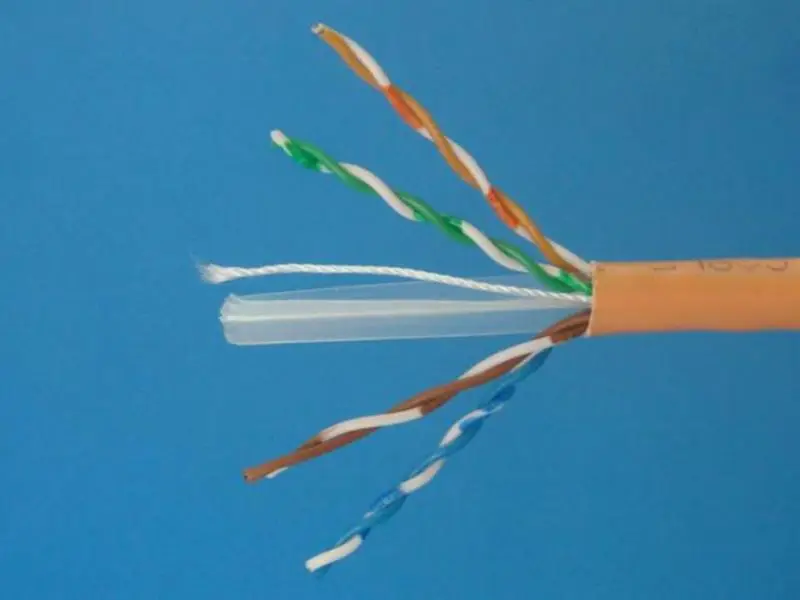
An Ethernet cable, specifically the Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) variety, is the standard for wired network connections due to its robustness and effectiveness. These cables are composed of multiple insulated copper wire pairs twisted around each other, a design that helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. The UTP cable’s outer layer is typically covered by a plastic jacket that protects the wires and enhances the cable’s durability. Inside, the colour-coded wire pairs are arranged in a specific pattern, ensuring organised and efficient data transmission. The RJ-45 connectors at both ends of the cable click into place, providing a secure connection to network devices such as routers, switches, and computers. This simple yet effective design has made the UTP Ethernet cable a staple in home, office, and data centre environments for reliable network communication.
Also read: Is Ethernet a network protocol? Exploring its capabilities and impact
How ethernet cables work
Ethernet cables work by transmitting electrical signals that represent data across a network. Here’s a step-by-step look at the process:
Data transmission: Data is sent from a device through an ethernet cable to a network switch or router.
Signal integrity: The twists in the cable help maintain signal integrity by reducing crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
Ethernet protocol: The data is encapsulated following the ethernet protocol, which includes a header with control information and a payload with the actual data.
MAC addresses: Each device on the network has a unique Media Access Control (MAC) address, which the ethernet cable uses to direct the data to the correct destination.
Reception: The receiving device interprets the signal and extracts the data, which is then processed or stored as needed.
Types of ethernet cables
Ethernet cables are classified into various categories, each denoting the cable’s performance and maximum data transmission capabilities. Categories such as Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat7 indicate the cable’s specifications, with higher categories offering increased speeds and enhanced resistance to interference, ensuring reliable data transmission in networking environments.
Also read: Ethernet dedicated lines vs. wireless networks
Advantages and disadvantages of ethernet cables
Ethernet cables are reliable in data transmission, supporting high-speed gigabit rates for bandwidth-intensive applications. They are cost-effective and widely used in networking, ensuring easy integration.
Ethernet cables have distance limitations, effective up to around 100 meters, with potential signal degradation beyond. They may experience interference in electromagnetic environments despite twisted pair design.