- Cloud computing enables users to store, access, and process data over the internet, offering benefits such as cost-efficiency, scalability, flexibility, and enhanced security. It is divided into public, private, and hybrid models, catering to different business needs.
- Cloud computing powers industries like e-commerce, healthcare, education, and finance, driving innovation through AI, machine learning, and serverless computing. The future of cloud includes advancements like quantum computing and deeper AI integration, further transforming business operations and service delivery.
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals interact with technology, enabling them to store, access, and process data over the internet instead of relying on local servers or personal devices. As a result, organizations can scale more efficiently, reduce costs, and innovate faster. Whether you’re a business leader seeking to enhance operational efficiency, or a tech enthusiast curious about this transformative technology, understanding cloud computing is essential in today’s digital-first world.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into cloud computing, covering its definition, benefits, key types, and real-world applications. Along the way, we’ll also highlight some important concepts and advancements related to cloud computing that are shaping the future of technology.

What is cloud computing?
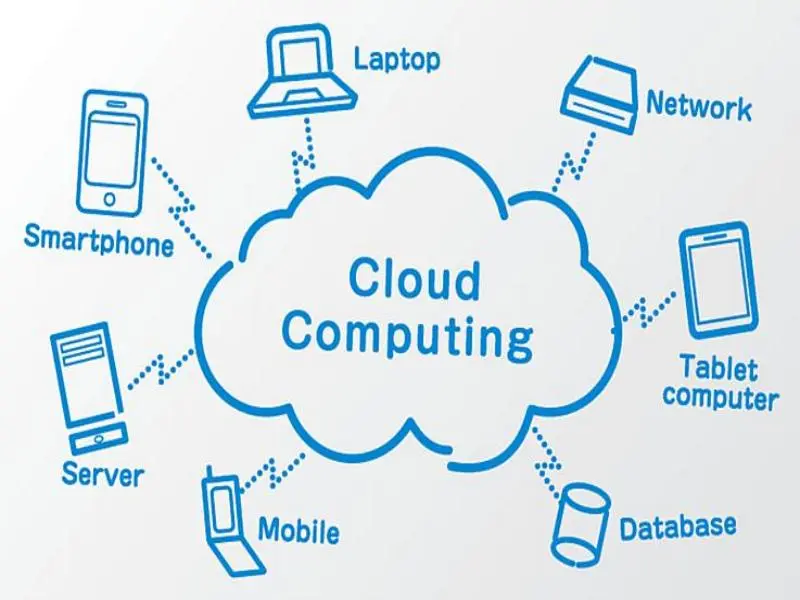
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as storage, processing, and networking over the internet, or “the cloud.” Instead of hosting applications, storing data, or managing servers on physical hardware, users access these services through a cloud provider’s infrastructure.
Cloud services allow organizations to scale their IT resources up or down depending on demand, improving both flexibility and cost-efficiency. Additionally, individuals can access their data and software from virtually any device, anywhere with an internet connection, making cloud computing a fundamental part of the modern digital ecosystem.
Also read: Addressing cloud computing vulnerabilities: Securing data
Also read: What is hardware virtualisation in cloud computing?
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing offers a range of benefits to both businesses and individuals. Below are some of the most significant advantages of leveraging cloud services.
- Cost-Efficiency: Traditional IT infrastructure requires substantial upfront investments in hardware, software, and the manpower to maintain them. With cloud computing, businesses can save on these capital expenses by adopting a subscription-based model. Most cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go services, which means businesses only pay for the resources they actually use. Additionally, cloud services reduce operational costs by eliminating the need for on-site data centers, reducing power consumption, and minimizing maintenance costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: One of the most compelling reasons businesses turn to cloud computing is its scalability. Unlike traditional systems that require physical upgrades to handle increasing demand, cloud services allow businesses to scale their operations quickly and easily. Whether you need more storage, processing power, or even an entirely new software solution, the cloud can meet those demands in real-time without interruption.
- Accessibility and Mobility: Cloud computing allows users to access their data and applications from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection. This makes it incredibly convenient for remote work, business continuity, and global collaboration. Teams can work on shared documents, access applications, and interact in real-time from different locations, boosting productivity.
- Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in robust security measures, often providing better protection than traditional on-premises solutions. Features like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and advanced firewalls ensure that your data is protected from cyber threats. Cloud services also typically offer automatic backups, making data recovery more straightforward in case of an emergency.
Also read: Oracle to invest over $1B on AI, cloud computing in Spain
Also read: Edge or cloud computing? What are the differences?

Types of cloud computing
Cloud computing comes in different forms, each catering to various needs. Understanding these types is crucial for businesses deciding which cloud services best meet their requirements.
- Public Cloud: Public cloud services are owned and operated by third-party providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. These providers offer cloud resources like storage, computing power, and software applications to the public, often on a pay-as-you-go basis. Public clouds are ideal for businesses that need to quickly scale up without large upfront investments. Since the resources are shared among multiple users, they tend to be cost-efficient.
- Private Cloud: A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted either on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds are often preferred by organizations with strict security requirements, such as healthcare, finance, and government sectors.This model provides more control over data and resources but requires higher investments in infrastructure and management.
- Hybrid Cloud: The hybrid cloud is a combination of public and private cloud services. It allows businesses to move workloads between both environments, depending on their needs. For instance, an organization might store sensitive data on a private cloud for security reasons while using a public cloud for less critical workloads. This flexibility gives businesses the ability to optimize their IT infrastructure, balancing cost-efficiency with security.
- Multicloud: Multicloud refers to the use of multiple cloud services from different providers to avoid vendor lock-in and enhance redundancy. A multicloud strategy can improve resilience, reduce downtime, and offer more flexibility in choosing the best services available from different providers.
The cloud is not just a technology. It’s a platform that empowers organizations to innovate faster and more efficiently than ever before.
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
Key technologies driving cloud computing
Several technologies are critical in enabling the functionality and growth of cloud computing. Here are some of the key technologies driving cloud adoption today:
- Virtualization: Virtualization allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine, enabling more efficient use of resources. In cloud computing, this technology allows providers to allocate resources dynamically based on demand. This not only optimizes the use of infrastructure but also helps in scaling cloud services efficiently.
- Containers and Kubernetes: Containers package an application and its dependencies into a single unit, making it easier to deploy and run across various computing environments. Kubernetes is an open-source platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Together, containers and Kubernetes help cloud providers offer highly scalable, efficient, and portable solutions.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing refers to processing data closer to the source of data generation, such as IoT devices or sensors, rather than sending all the data to centralized cloud servers. By processing data at the edge, businesses can reduce latency, optimize bandwidth, and improve performance. This is particularly valuable for applications that require real-time data processing, like autonomous vehicles and industrial IoT.
Also read: Akamai connected cloud offers an approach to cloud computing

Real-world applications of cloud computing
Cloud computing powers numerous industries and applications, offering a wide range of benefits that extend far beyond just storage. Here are some real-world use cases of cloud computing:
- E-Commerce: E-commerce platforms rely heavily on cloud computing for data storage, payment processing, and customer relationship management (CRM). The scalability of cloud services allows e-commerce businesses to handle spikes in traffic during events like Black Friday or Cyber Monday without worrying about server overloads.
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry has seen massive growth in the adoption of cloud computing, primarily due to the need for secure data storage and management of patient information. Cloud services allow healthcare providers to store patient data in a compliant, secure manner while enabling better collaboration and faster decision-making. Additionally, cloud computing powers telemedicine platforms, health monitoring devices, and data analytics that drive predictive health care.
- Education: Cloud computing has transformed the education sector by providing students and educators with access to learning management systems (LMS), virtual classrooms, and collaboration tools. The scalability and flexibility of cloud services have enabled educational institutions to expand access to education, providing tools for online learning, research, and student collaboration from anywhere in the world.
- Finance and Banking: Financial institutions are increasingly using cloud computing to enhance their data analytics capabilities, improve security, and automate tasks. Cloud technology supports financial applications, from risk analysis and fraud detection to customer service and investment strategies. It also enables financial institutions to meet regulatory compliance standards more easily.
Future trends in cloud computing
As technology continues to evolve, cloud computing will only become more integral to our digital lives. Here are some key trends that are shaping the future of cloud computing:
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Cloud providers are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) capabilities into their offerings. These technologies allow businesses to analyze large datasets, automate decision-making, and gain valuable insights. As cloud platforms continue to incorporate AI, businesses can leverage these tools to drive innovation and enhance customer experiences.
- Serverless Computing: Serverless computing abstracts the underlying infrastructure, allowing developers to focus purely on writing code without managing servers. This innovation simplifies application development, reduces costs, and improves scalability, enabling businesses to scale automatically as demand increases.
- Quantum Computing in the Cloud: Quantum computing, which leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to solve problems faster than classical computers, is an emerging trend in the cloud. Major cloud providers like IBM, Google, and Microsoft are investing heavily in quantum computing as it holds the potential to revolutionize industries such as finance, pharmaceuticals, and logistics by solving complex problems in seconds.
The beauty of the cloud is that it allows you to innovate without the constraints of traditional infrastructure. It is a powerful tool for driving change and growth.
Andy Jassy, CEO of Amazon Web Services
How cloud computing is transforming business and innovation?
Cloud computing has radically reshaped the way businesses and individuals store, access, and process data. Traditionally, businesses had to invest heavily in physical infrastructure, including servers, data centres, and dedicated IT teams, to manage and store information. However, cloud computing has eliminated these barriers, offering scalable and flexible solutions that allow companies to access powerful computing resources over the internet. This transformation has made it possible for organisations to take full advantage of advanced technologies without the significant costs and complexities of maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
Moreover, cloud computing enables businesses to harness the power of cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and even quantum computing. Cloud platforms provide the necessary computing power and storage to run complex AI models and data analytics, empowering businesses to innovate and improve customer experiences. The ability to leverage these technologies without substantial upfront investments allows organisations to stay at the forefront of technological advancements.
Whether it’s improving accessibility for remote workers, scaling e-commerce operations, or enabling the development of cutting-edge technologies like AI and quantum computing, the impact of cloud computing is undeniable. By understanding its core principles, benefits, and applications, businesses and individuals alike can better harness the power of the cloud to thrive in today’s digital economy.
In conclusion, cloud computing has become a catalyst for business transformation. By improving accessibility for remote work, enhancing scalability for growth, and enabling the development of advanced technologies, the cloud has become an essential tool for businesses and individuals alike. Understanding its core principles, benefits, and applications will enable organisations to thrive in today’s ever-evolving digital landscape. As cloud solutions continue to evolve, their impact on driving innovation and shaping the future of business will only grow.
Also read: Cloud computing and IoT: How do they work together?

FAQs: What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services such as storage, processing power, and software over the internet, allowing users to access and manage data remotely without relying on local hardware.
The primary types of cloud computing are public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multicloud, each offering different levels of scalability, control, and cost-efficiency.
Cloud providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication, to protect data. However, businesses must also follow best practices for securing their cloud environments.
Cloud computing benefits a wide range of industries, including healthcare, finance, e-commerce, education, and manufacturing, by improving efficiency, scalability, and innovation.
The future includes deeper integration with AI and machine learning, the rise of serverless computing, advancements in edge computing, and the exploration of quantum computing for solving complex challenges.