- 5.5G, introduced by Huawei at MWC 2024 as 5G-Advanced, represents a critical stage between 5G and 6G, significantly enhancing speed, latency, reliability, and connectivity.
- It brings new capabilities such as integrated sensing and communication, ultra-high-speed internet, and extensive IoT support, transforming industries like autonomous driving, smart cities, and healthcare with real-time remote operations and intelligent infrastructure.
- While 5.5G requires new devices and upgraded infrastructure, it complements 5G and prepares the groundwork for the future 6G network, driving digital transformation and economic growth.
The concept of 5.5G, officially termed 5G-Advanced (also known as 5G-A or 5.5G), was first introduced by Huawei at this year’s Mobile World Congress (MWC 2024). “5G is on the right path to business success,” said Li Peng, Huawei’s corporate senior vice president and president of ICT sales and services, at Mobile World Congress 2024 in Barcelona. “5.5G is entering commercial use in 2024 and, as 5.5G, AI, and cloud converge, carriers can unlock the potential of new applications and capabilities.” 5.5G is a critical phase in the evolution from 5G to 6G, bringing improvements in capacity, speed, latency, and reliability. It represents a comprehensive upgrade over 5G, incorporating technologies like integrated sensing and communication, integrated communication and computation, and integrated air-space-ground communication. By extending the capabilities of 5G, 5.5G aims to revitalise digital life and support industrial digital transformation. The primary enhancements are as follows:
Faster Speeds: The peak speed of 5.5G can reach up to 10 times that of 5G, with network access speeds up to 10Gbps and millisecond-level latency.
Better Service: Users will receive prioritised service based on specific business needs, ensuring tailored communication services for different customer groups.
There are so many use cases, in logistics, warehousing, and factories that we haven’t quite been able to reach with 5G. This is where 5.5G will come in and propel us into other areas.
Alexander Lehrmann, senior director of innovation & development at Sunrise, a Swiss telecoms company
Superior Products: Real-time 3D rendering, game content loading, and cloud collaboration will be accelerated, significantly enhancing the functions and experiences of new 5G calls, cloud phones, and cloud computers.
Enhanced Perception: Integrated sensing and communication will advance the network from single data transmission to comprehensive multi-dimensional sensing, meeting users’ needs across water, land, and air scenarios.
Broader Connectivity: By integrating new passive IoT networking technologies, 5.5G transitions from point-to-point communication to ultra-long-distance, large-scale passive IoT, catering to modern asset management needs.
Stable Control: The deterministic network ensures high reliability and low latency for critical data transmission, meeting the precise control and collaborative operation demands of users.

5.5G solutions are being trialled with major operators all over the world
Currently, Huawei’s full-series, all-scenario 5.5G solutions are being trialled with major operators in China, the Middle East, Asia-Pacific, and Europe. In China, the three major operators are also actively advancing 5.5G. On March 28, China Mobile launched the world’s first 5G-A commercial deployment in Hangzhou, announcing the initial list of 100 cities with 5.5G networks, with plans to expand to 300 cities within the year. China Telecom has begun industry application scenario validation, such as enabling mining applications in Shaanxi. China Unicom released ten innovative 5G-A demonstration projects to explore 5G-A technologies and business models.
5.5G offers more than just incremental improvements over 5G. With each half-generation advancement, network speed increases by approximately ten times, driving industrial upgrades. As an intermediate stage between 5G and 6G, 5.5G enhances 5G’s capabilities through improved RF, software upgrades, and AI, using the 6GHz frequency band to significantly boost speed, latency, and efficiency.
5.5G introduces features like downlink speeds of 10Gbps, uplink speeds of 1Gbps, and millisecond-level latency, supporting extensive IoT connections and enhanced terminal sensing and positioning capabilities. These advancements extend beyond traditional communication to support new applications requiring large bandwidth and low latency, such as extended reality (XR) and holographic interactions.
The commercial deployment of 5.5G began in 2024
The commercial deployment of 5.5G began in 2024, aiming to accelerate 5G adoption. The market demand for 5.5G is driven by the limitations of 5G in handling complex network requirements for applications like autonomous driving and high-end manufacturing. For instance, the network traffic for smart cars in assisted driving scenarios is expected to exceed 300GB per month, which 5G cannot adequately support.
5.5G does not replace 5G but complements it, offering enhanced features where needed while preparing for 6G. It maintains the same network architecture as 5G but improves performance through RF modifications, software upgrades, and AI, ensuring adaptability to various business needs.
The development of 5.5G technologies also serves as a foundation for 6G, which is still in the research phase. By nurturing new business models and technologies, 5.5G lays the groundwork for the intelligent connectivity envisioned for 6G.
While the 5.5G industry chain is maturing, further integration is needed. Future developments will support applications like naked-eye 3D, extended reality, low-altitude economy, and intelligent shipping, driving digital economic growth. Industry stakeholders must prepare in terms of standards, spectrum, products, applications, and ecosystem development to fully realise 5.5G’s potential.
Alexander Lehrmann, senior director of innovation & development at Sunrise, a Swiss telecoms company, said: “There are so many use cases, in logistics, warehousing, and factories that we haven’t quite been able to reach with 5G. This is where 5.5G will come in and propel us into other areas.”
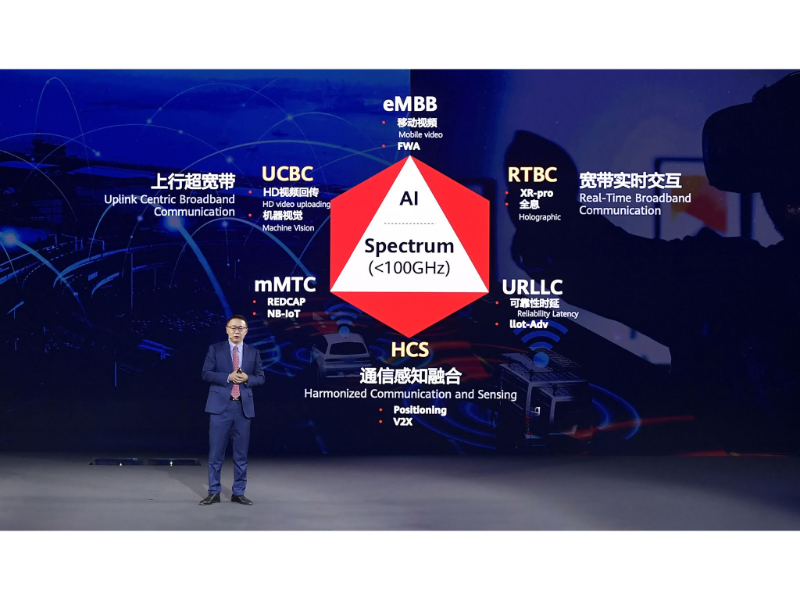
Five key enhancements of 5.5G
High-Speed, Low-Latency Communication: 5.5G will improve communication speeds and reduce latency, enhancing real-time interactions, HD video streaming, and VR applications, thus promoting sectors like gaming, online education, and remote work.
IoT Development: 5.5G will support more IoT devices with stable and efficient data transmission, accelerating the growth of smart homes, smart cities, and intelligent logistics, further driving digital transformation.
Heterogeneous Network Integration: 5.5G will integrate different networks (5G, WiFi, satellite) to provide broader coverage and more stable connections, facilitating cloud computing, edge computing, and big data analytics, fostering innovation in emerging industries.
AI Integration: Combining AI with 5.5G will enable more intelligent and automated applications, such as smart manufacturing and intelligent supply chains.
Enhanced AR/VR: Higher bandwidth and lower latency will advance AR/VR technology, offering immersive experiences in gaming, education, and training, and creating new business opportunities.
A noticeable improvement in user experience
With faster network speeds, 5.5G offers a noticeable improvement in user experience. While current 5G can theoretically reach 1Gbps, real-world conditions often lead to network delays and congestion, especially during peak times or on fast-moving trains. In contrast, 5.5G aims to provide theoretical speeds up to 10Gbps, greatly enhancing experiences in ultra-HD video and online gaming.
Self-Optimising Networks: 5.5G introduces AI models for network self-optimisation and self-repair. This capability allows networks to automatically identify and resolve issues, ensuring stability and reliability, and dynamically adjust resources based on user demand.
Convenience and Connectivity: 5.5G enhances connectivity, supporting more devices simultaneously without performance degradation. This facilitates seamless connections across various devices and introduces passive IoT, allowing objects with passive tags to communicate with 5.5G base stations up to 200 meters away, crucial for large-scale IoT deployments.
5G is on the right path to business success. 5.5G is entering commercial use in 2024 and, as 5.5G, AI, and cloud converge, carriers can unlock the potential of new applications and capabilities.
Li Peng, Huawei’s corporate senior vice president and president of ICT sales and services
“5.5G+” and New Productivity: The advent of 5.5G brings new opportunities for emerging industries. Technologies like XR, the metaverse, smart cities, smart homes, and remote healthcare are expected to experience significant growth. For instance, 5.5G’s integrated sensing and communication technology enables intelligent transportation, providing real-time information about traffic conditions, reducing congestion, and improving overall efficiency. In healthcare, 5.5G supports real-time remote surgery guidance and VR training for medical professionals, optimising resource distribution.
Upgrading Devices and Infrastructure: To benefit from 5.5G, users will need new devices with updated chips. Existing 5G chips cannot support the enhanced features of 5.5G. Similarly, network infrastructure will require upgrades or new builds to accommodate 5.5G capabilities, starting with high-demand areas and expanding to broader regions.
Commercial Rollout: The commercial rollout of 5.5G is already underway, with initial deployments in places like the Hangzhou Asian Games, where it supported applications like naked-eye 3D viewing and high-density network usage. Major cities like Shanghai are also advancing 5.5G coverage, ensuring hotspots and tourist areas benefit from enhanced network performance.
As 5.5G becomes commercially available, users will gradually experience its benefits, from improved personal connectivity to transformative applications across various industries.
5.5G, bridging 5G and 6G, boosts speed, latency, and connectivity, enabling advanced IoT, smart cities, and real-time remote operations.

