- Information security is an eternal hot topic, and the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) has been facing vulnerability exposure for a long time. It’s worth understanding about a new encryption framework, Resource Public Key Infrastructure, or RPKI.
- Network operators employ truth-based mechanisms such as peer-to-peer protocols and manual routing filtering to reduce the risk of BGP hijacking, and while effective to a certain extent, these solutions are themselves limited.
- By harnessing the power of cryptography, RPKI provides a standardized and scalable solution to the ongoing challenges posed by BGP vulnerabilities.
OUR TAKE:
RPKI represents a monumental leap forward in Internet routing security, utilizing cryptography to provide a standardized and scalable solution to the persistent challenges posed by BGP vulnerabilities.
–Fei Wang, BTW Reporter
Why do we need RPKI?
When it comes to network information security, you may have heard of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), yet as the backbone of Internet routing, BGP has long faced vulnerability exposure, leaving it open to manipulation and hijacking. Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) is an encryption framework designed to strengthen BGP and protect Internet routes from malicious actors.
Also read: What is Routing Information Protocol (RIP)?
The underlying BGP is the protocol that connects the Internet backbone and helps routers determine the most efficient path for packets to travel across the Internet. It exchanges routing information between networks (autonomous systems), similar to the way GPS communicates with satellites and other GPS devices to provide accurate navigation directions. Routers advertise their available routes to neighboring routers through BGP messages. These messages contain information about reachable IP prefixes and the path to reach them. Then, neighboring routers use this information to update their routing table, and determine the destination IP address forwarding flow optimal path.
Also read: Security, anonymity and stability: Why proxy servers are an increasingly popular internet tool
But one scenario we can’t ignore is if a rogue entity infiltrates an Internet service provider’s network and fraudulently announces the wrong routing of IP prefixes. Suddenly, legitimate traffic is diverted to undesirable destinations, causing chaos and compromising the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of online services.This insidious phenomenon, sometimes referred to as BGP hijacking, highlights the urgent need for strong security measures to protect Internet routing.
Here’s an example: In February 2008, to carry out a government order, Pakistan Telecom mistakenly announced a BGP route to redirect YouTube traffic to its own servers. Unfortunately, the upstream provider receiving the route accepted it unverified and then passed on the information, thus spreading the wrong route across the Internet until almost everyone using the Internet believed that facebook had moved its servers into the Pakistani network.The blunder not only crippled YouTube, but also left Pakistan’s Internet Service Provider (ISP) in a bind, which soon received millions of requests from YouTube’s users.
Because BGP does not guarantee the authenticity of routing advertisements, hackers’ deliberate attacks and incorrect configuration of network parameters can lead to route hijacking. AS the next key Internet security infrastructure deployed by ICANN after DNSSEC,RPKI constructs an IP address resource authorization authentication system from the perspective of IP address resource management to verify whether the routing advertising of a specific IP address prefix is legitimate, and provides an interzone routing security scheme (such as S-BGP and BGPS) EC) implementation provides a trusted source of information.
Ma Di, China Internet Network Information Center
Existing solutions: IRR, BGPsec, RPKI
Network operators employ trust-based mechanisms such as peer-to-peer protocols and manual route filtering to reduce the risk of BGP hijacking, and while effective to a certain extent, these solutions are inherently limited and rely on human oversight and cooperation to maintain the integrity of routes. One such elastic solution is to filter using the information available in the Internet Routing Registry (IRR). IRR is a public database of routing information provided by Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) and third-party vendors. However, this solution has some limitations, because third parties in the game cannot systematically maintain the data.
Border Gateway Protocol Security (BGPsec) is another advanced solution that is a secure extension of BGP as defined in RFC 8205. In BGPsec, the AS_PATH attribute is replaced with the new BGPsec_Path attribute, which provides a way to cryptographically validate routes received from peers.
Advanced solutions rely on the Resource Public Key Infrastructure (RPKI) for cryptographic authentication of routing information.
Pop quiz
Which is not an existing solution to the BPG crisis?
A. BGPsec
B. RPKI
C. AS
D. IRR
The answer is at the bottom of this article.
What is RPKI
You can think of RPKI as a passport and visa control system for Internet traffic. Routing information like the Internet destination or country.Just as we need a valid passport and visa to legally enter a particular country, Internet routers require a valid encryption certificate and Routing Origin Authorization (roa) issued by the RPKI to announce and verify IP prefixed. The cryptographic certificate acts as a passport to verify the identity of the IP address holder, while the roa acts as a visa to authorize the legitimate origin of the IP prefix.Without the correct “passport” (encrypted certificate) and “visa” (ROA), Internet routers cannot securely announce routes (IP prefixes) to specific destinations, thereby preventing unauthorized traffic and ensuring that packets reach their intended destination safely and efficiently. With RPKI enabled, network operators and routers act as vigilant border control agents, verifying the legitimacy of routing notices before storing and disseminating them, thereby preventing unauthorized traffic from entering or leaving a specific “country” (IP prefix) on the Internet.
Also read: What is the RIPE NCC?
How RPKI works for APNIC Regional Internet Registry
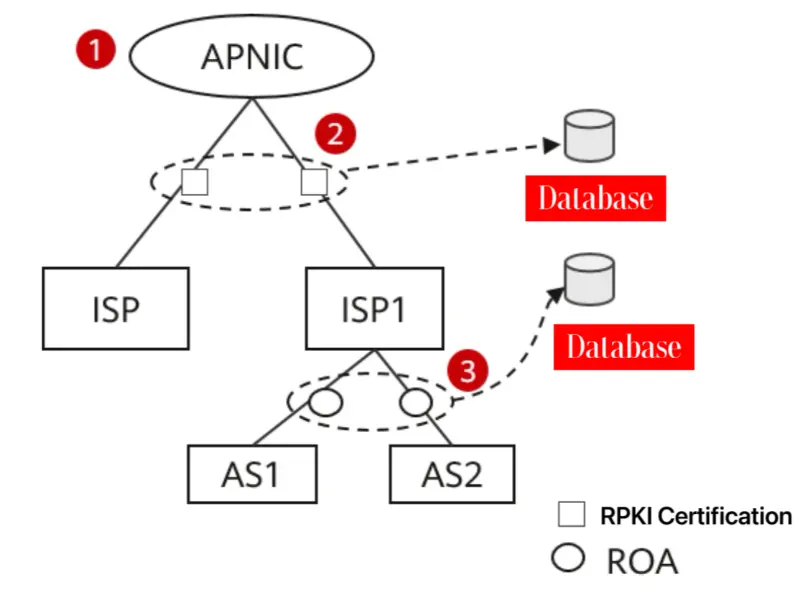
The certificate issuance system of RPKI corresponds to the Internet number resource allocation architecture, as shown in the figure above. The certificate issuance system authorizes resources by issuing resource certificates from top to bottom. The content of the certificate includes the binding relationship between the IP address prefix/AS number and the receiving institution, indicating that the resource holder has been legally authorized to use this part of the number resources.
RPKI operates on a hierarchical model, wherein Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) serve as the top-level authorities responsible for managing Internet number resources. These resources include IP address blocks and Autonomous System Numbers (ASNs), which are essential components of Internet routing. RIRs issue cryptographic certificates to resource holders, binding their IP address allocations to cryptographic keys. These certificates are then used to generate Route Origin Authorisations (ROAs), which specify the legitimate origins of IP address prefixes.
Why is RPKI important?
The adoption of RPKI has brought many benefits to the Internet ecosystem. RPKI provides a mechanism to verify the authenticity of route announcements, which can prevent BGP hijacking and route leakage, and improve the security and stability of Internet routes. In addition, RPKI gives network operators control over their routing policies, ensuring that traffic flows along the intended path and minimizing the risk of misconfiguration or malicious activity.
Benefits of RPK
A. Much safer than manually checking the Whois Database or the lRR database.
B. Secure origin of the prefix or origin-as is the first step to preventing many attacks on BGP integrity.
C. Instruction/information from the resource custodian can be cryptographically verified (for example,Letter of Authority signing).
Q: How can an internet border router synchronize with a server for validation of RPKI routers?
Are there any public servers to consult it?
“What happens with the repository,there is a software that is a intermediary between LACNIC and the routers. That is the RPKI validator, was one in the port project developed with Mexio, and so it makes available the information cryptographically validated to the border routers. The relation between the border router– it is of ectreme trust because the closeness and the security between a border router and a validator to be good. It’s not recommended to use validators for your routers since there are public validators, but it’s to see what the validator looks like etc. It’s not for you to connect it with a border router.” Gianina Pensky, Head of Registration Services, replied in LACNIC webinar-Network Security with RPKI.
So, RPKI represents an important area of development for Internet routing security. By harnessing the power of cryptography, RPKI provides a standardized and scalable solution to the ongoing challenges posed by BGP vulnerabilities. As we continue to grapple with a complex digital environment, the adoption of RPKI is a critical step toward building a more secure, resilient and trusted Internet infrastructure.
The correct answer is C.

