- Augmented reality was created in the 1950s and has evolved significantly, from its conceptualisation to modern applications and future prospects, offering enhanced user experiences across various industries.
- Its integration with AI and machine learning has further boosted its capabilities, promising personalised and intuitive interactions.
- Despite challenges like privacy concerns and technical hurdles, AR’s continued evolution signifies a transformative journey, bridging the digital and physical worlds for unprecedented human experiences.
Augmented reality has garnered increasing interest, particularly over the past decade, owing to its wide-ranging applications across multiple industries. It serves as a tool for enriching natural environments and scenarios, enabling interactive experiences within real-world contexts.
The significance of AR in today’s technological landscape is undeniable, spanning from recreational gaming and entertainment to more pragmatic applications in education, healthcare, and industrial sectors. By seamlessly integrating digital components into reality, AR facilitates enhanced experiences, offering users interactive and easily manipulable environments. It revolutionises human interactions with the physical world, enhancing perceptions and enriching experiences. In the following section, we will explore the augmented reality from the time it was created.
Also read: What is Augmented Reality?
Also read: How do autonomous vehicles work?
Also read: What is Web3 gaming?
When was augmented reality created?
Tracing back to its roots, the inception of augmented reality can be traced to earlier conceptualisations preceding the contemporary technology. Although the term “augmented reality” had yet to be coined, the foundations were laid in the mid-20th century. An early precursor was Morton Heilig’s Sensorama, developed in the 1950s, which provided an immersive multisensory experience, albeit not in the modern AR sense.
Morton Heilig’s innovation did not end with Sensorama; he furthered his endeavours by inventing the Telesphere Mask in 1960, considered the first head-mounted display (HMD). While lacking electronic integration, this device offered stereoscopic 3D visuals, expansive vision, and stereo sound, hinting at the potential for technology to enhance sensory perception. These early developments laid the groundwork for the evolution of modern augmented reality.
In the quest to identify the pioneers of contemporary augmented reality, Ivan Sutherland emerges as a pivotal figure. In 1968, Sutherland, alongside his student Bob Sproull, developed what is often regarded as the first AR/VR headset, named the Sword of Damocles. Suspended from the ceiling, this headset displayed simple wireframe drawings overlaid onto the physical world. Despite its rudimentary nature, the Sword of Damocles represented the first instance of computer-generated overlays in conjunction with real-world environments, marking the inception of both virtual reality and augmented reality.
Augmented reality in the late 20th century
The 1990s marked a pivotal era in the development of augmented reality, witnessing the formalisation of its foundational concepts. It was during this time that Boeing researcher Tom Caudell officially coined the term “augmented reality” to describe a digital display system he was creating to aid in wiring harness assembly. This period saw significant strides in computer technology, fostering the growth of AR research and development.
In the domain of gaming and entertainment, AR made notable advancements, exemplified by Columbia University’s KARMA (Knowledge-based Augmented Reality for Maintenance Assistance) system introduced in 1992. Utilising a see-through, head-mounted display, KARMA guided users through maintenance and repair tasks by overlaying textual instructions and diagrams directly onto machinery, showcasing an early practical application of AR.
The advent of more powerful computers accelerated AR’s evolution, enhancing its capability to overlay computer-generated images onto the real world in real-time. By the late 1990s, AR transitioned from research labs to practical real-world applications, recognised for its potential to enhance user interaction with both physical and digital realms. This recognition spurred innovations that would shape the augmented reality landscape in the 21st century.
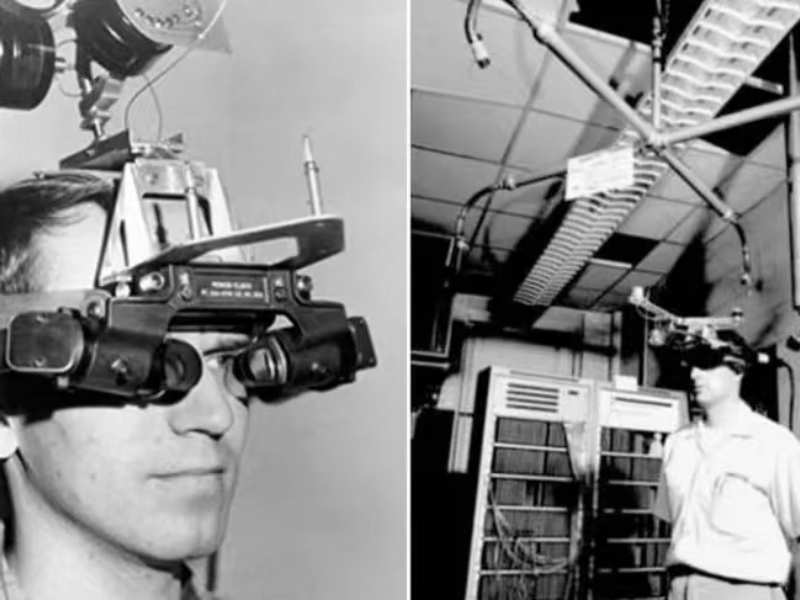
Continued experimentation and innovation by researchers and developers led to the development of the first AR systems integrating software predictive tracking and collaborative multi-user environments. The groundwork laid during this period set the stage for the subsequent surge in AR technology in the 21st century, as it found applications across diverse fields spanning medicine, entertainment, and beyond.
The boom of the 21st century
In an era dominated by smartphones and mobile computing, augmented reality (AR) found a fertile ground for its evolution and expansion. The integration of AR with mobile devices opened up new avenues for user interaction and application development, democratising access to AR from a niche technology confined to labs to a ubiquitous tool for enhancing digital interactions in everyday life.
The 21st century witnessed significant milestones and advancements in AR technology. In 2008, the launch of Wikitude marked the debut of the first mobile app utilising AR. Wikitude empowered users to access information about their surroundings by simply pointing their mobile phones at locations, heralding the integration of AR into mainstream consumer technology and unlocking endless possibilities for interactive user experiences.
The emergence of notable AR applications further propelled the technology’s evolution. In 2016, the release of Pokémon GO captivated global audiences, leveraging AR to overlay virtual creatures onto the real world through smartphone screens. This phenomenon not only captivated millions but also introduced the masses to the concept of AR, elevating its visibility and acceptance.
Each innovation in this period underscored AR’s transformative potential, extending beyond gaming to revolutionise navigation, education, retail, and more. From enhancing gaming experiences to offering practical solutions in various industries, AR showcased its versatility and became an integral part of the digital landscape, promising a future where virtual and physical realities seamlessly merge.
Modern applications and augmented reality
Today, augmented reality permeates diverse sectors, transcending its origins in gaming and entertainment. Industries such as healthcare, education, retail, and automotive leverage AR to enrich user experiences, drive efficiencies, and optimise processes. Bolstered by advancements in AI, machine learning, and computer vision, modern AR applications offer intuitive, interactive, and immersive experiences.
In healthcare, AR facilitates advanced surgical visualisation, patient education, and medical training. Technologies like Microsoft’s HoloLens aid surgeons in surgical planning and navigation, providing real-time 3D visualisations of patients’ anatomy during procedures. Similarly, AR transforms medical education, offering interactive learning experiences and deeper insights into complex medical concepts.
Retail and e-commerce sectors embrace AR to enhance customer engagement and purchasing decisions. AR apps enable virtual try-on experiences for clothing, accessories, and cosmetics, while IKEA‘s app allows customers to visualise furniture in their homes before buying. These applications not only boost customer satisfaction but also reduce returns and enhance informed decision-making.
In education, AR revolutionises traditional learning methods, making subjects more engaging, visual, and interactive. Whether visualising scientific concepts, exploring historical events, or learning languages, AR brings learning to life, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Moreover, AR facilitates remote learning, providing students with immersive experiences beyond traditional classrooms.
The impact of AI and machine learning on AR evolution
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning play pivotal roles in advancing augmented reality (AR). These technologies empower AR applications to recognise patterns, process vast data, and deliver contextually relevant digital overlays, resulting in more intuitive and personalised user experiences. This synergy marks a significant milestone in AR’s development.
AI-driven object recognition and computer vision are instrumental in accurately overlaying digital content onto the real world in AR applications. For example, AI algorithms enable social media filters to precisely identify facial features and movements for interactive user experiences. In retail, AI-powered AR apps recognise products and provide real-time information, enhancing the shopping experience.
The integration of AI and machine learning with AR extends beyond user experiences, offering new possibilities in data analytics and insights. Businesses can leverage AI-powered AR to gather real-time data on user interactions and preferences, informing strategies and product developments. However, challenges such as privacy, data security, and ethical concerns must be addressed to ensure responsible and sustainable AR development and adoption.
Future outlook and challenges
As AR evolves, fuelled by advancements like 5G and IoT, it is poised to become an integral part of daily life, offering enhanced experiences. However, challenges including privacy, data security, and technological advancements persist. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical considerations is crucial for responsible AR development.
Technical challenges, such as improving realism and interactivity, and developing ergonomic wearable devices, must be addressed to realise AR’s full potential. Despite these challenges, the future of AR holds promise, ushering in an era where digital and physical realities converge to unlock new opportunities for innovation and human advancement.
Conclusions
As we contemplate augmented reality’s journey, tracing back to its creation, spanning from its conceptual roots to contemporary applications and future prospects, it becomes evident that AR transcends mere technological innovation. It serves as a conduit between the digital and physical realms, offering unparalleled avenues for interaction, communication, and experience. Each phase of AR’s progression builds upon preceding advancements, propelled by a convergence of technological innovation, imaginative applications, and societal acceptance.
The evolution of AR chronicles humanity’s persistent quest to surpass the limitations of our senses and experiences. Looking ahead, the continued evolution of AR promises not only enhanced ways of perceiving and engaging with the world but also the emergence of novel dimensions of human experience, characterised by heightened interconnectedness, immersion, and augmentation.

