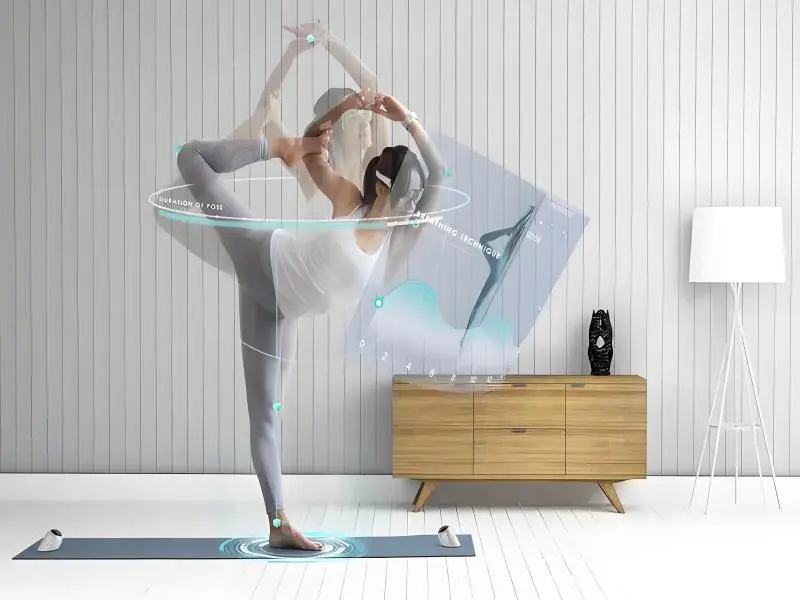
- Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing user experiences across various industries, from gaming to healthcare.
- Key technologies behind AR include cameras, sensors, processing power, and sophisticated software algorithms, which work together to create immersive environments.
Augmented reality (AR) has rapidly transformed from a niche technology to a mainstream innovation, reshaping industries and enhancing user experiences across various sectors. But what exactly is augmented reality, and how does it work? This article delves into the basics of AR, explores its applications, and looks ahead to how it could shape the future of technology and everyday life.
Also read: Augmented Reality (AR) in IT: Beyond gaming
Also read: Xreal unveils augmented reality glasses with custom chip
Understanding Augmented Reality (AR)
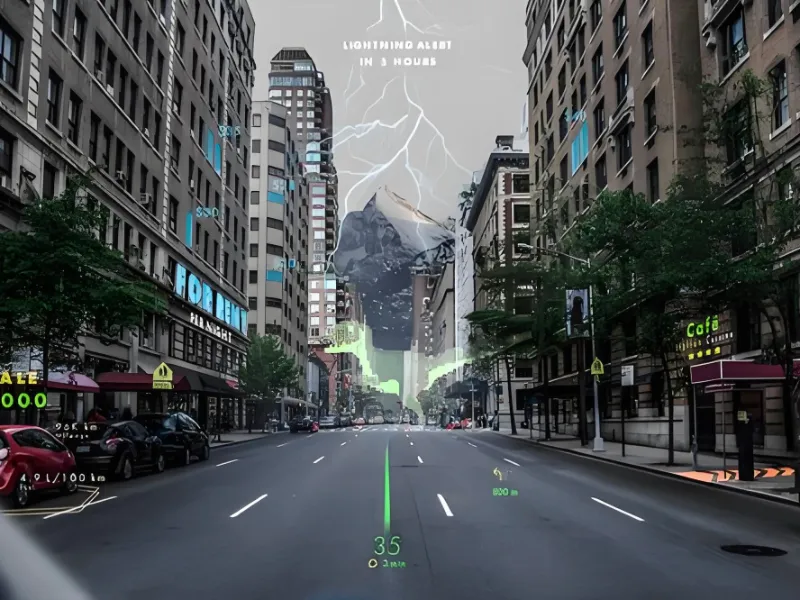

Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information—such as images, sounds, and other sensory data—onto the physical world in real-time. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses users entirely in a digital environment, AR enhances the real world with digital elements. These elements can be static (like images or text) or dynamic (such as 3D models or video), and they appear as if they exist within the user’s environment.
For example, AR is commonly used in smartphone applications where a digital object or piece of information appears on the screen when the camera is pointed at a particular object or location. Popular examples include Pokémon GO, where digital characters appear in the real world via your phone’s camera, or IKEA’s AR app, which lets you visualize furniture in your own home before making a purchase.
According to Rony Abovitz, founder of Magic Leap, “The magic of AR lies in its ability to change how we interact with the world around us—by blending physical reality with digital information.” This insight highlights the transformative nature of AR in enhancing real-world experiences.
How does Augmented Reality work?
At its core, AR relies on several technologies to create the illusion of digital content blending seamlessly with the real world. These include cameras, sensors, processors, and displays. The camera captures the real-world environment, while sensors track the device’s position and orientation. The processor then analyzes this data and renders the digital content, ensuring that it interacts appropriately with the environment in real-time. Finally, the display shows both the physical and digital elements, allowing the user to perceive the augmented reality experience.
As AR technology advances, it relies on more sophisticated motion tracking and depth sensing capabilities, making the experience even more immersive. For example, an AR app can recognize not only the shape of an object but also its texture, lighting, and surrounding space, making digital content appear more realistic and anchored in the real world.
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, emphasizes the potential of AR by stating, “AR is bridging the gap between the digital and physical world in ways that were once confined to science fiction. It has the power to reshape how we engage with our surroundings.” His statement underscores AR’s growing impact and its ability to transform how we perceive and interact with our environment.
The magic of AR lies in its ability to change how we interact with the world around us—by blending physical reality with digital information.
Rony Abovitz, founder of Magic Leap
Also read: Interview with Tu Yi, vice president and COO of EasyAR: Changing the future of augmented reality
Also read: Augmented reality on the road: Gamification or safety update?
The key technologies behind Augmented Reality
Several technologies play a crucial role in making AR experiences possible. These include:
1. Camera and sensors
The camera and various sensors (such as accelerometers and gyroscopes) are the eyes and ears of the AR system. They capture the user’s environment and track movement, ensuring that digital content is correctly aligned with the real world.
2. Processing power
AR systems require substantial processing power to analyze data and render 3D content in real-time. This is why many AR experiences rely on smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses, which have high-performance processors.
3. Displays
Displays—whether they are on smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses—show both the real world and the augmented content. Advances in display technology, such as OLED and microLED, have improved the quality and realism of AR visuals.
4. Software and algorithms
AR requires sophisticated algorithms to identify objects, track movements, and render digital content. These algorithms use computer vision, machine learning, and depth sensing to understand and interact with the physical world.
Also read: Application of augmented reality and mixed reality in life
Also read: What does the mesh do in augmented reality?
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented reality has found applications in a wide range of industries, transforming the way people interact with the world. From gaming to healthcare, AR is not just enhancing experiences but also creating entirely new opportunities for engagement, efficiency, and innovation. Below are some of the most prominent sectors that are leveraging AR technology.
1. Gaming and entertainment
One of the most well-known applications of AR is in the gaming industry. Games like Pokémon GO introduced millions of people to AR by allowing them to interact with virtual characters in real-world environments. AR enhances the gaming experience by superimposing digital elements in the physical world, creating a hybrid reality that deeply engages players. Beyond gaming, AR is making significant inroads in entertainment, including films, live events, and concerts. AR can be used to display virtual characters interacting with real-world objects or create dynamic visuals during performances, offering a more immersive experience.
John Hanke, the CEO of Niantic, which created Pokémon GO, notes, “Augmented reality is a natural extension of the gaming world. It brings the virtual into the real world, giving players a more meaningful and interactive experience.” This insight highlights how AR is redefining the boundaries of gaming and entertainment, where users are no longer confined to screens but can engage with their environment in exciting new ways.
2. Retail and e-commerce
AR is revolutionizing the way consumers shop, enabling them to try products virtually before purchasing. Retailers like IKEA have created AR apps that allow users to see how furniture will look in their homes before buying. Similarly, beauty brands like L’Oréal use AR to let customers try on makeup virtually, helping them choose products with more confidence and reducing the uncertainty of online shopping. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces return rates, benefiting both retailers and consumers.
Tim Cook, CEO of Apple, emphasizes the importance of AR in retail, stating, “Augmented reality allows customers to make more informed decisions by providing an interactive and personalized shopping experience. It’s not just a trend but a game-changer for retail.” Apple’s focus on AR underscores its growing influence in sectors like retail and e-commerce, where immersive digital experiences help businesses meet customer expectations in novel ways.
Augmented reality allows customers to make more informed decisions by providing an interactive and personalized shopping experience. It’s not just a trend but a game-changer for retail.
Tim Cook, CEO of Apple
3. Education and training

In education, AR is enhancing learning by providing interactive and immersive experiences. For instance, medical students can use AR to visualize 3D models of the human body, enabling a deeper understanding of complex anatomy. Similarly, history students can explore ancient civilizations through AR-enhanced textbooks, making learning more engaging. AR also plays a crucial role in hands-on training for fields like aviation, engineering, and military training, where real-world simulations are critical for skill development.
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, emphasizes AR’s transformative role in education: “Augmented reality is transforming education by making abstract concepts tangible and interactive. It allows students to experience what they learn, which enhances retention and comprehension.” As Nadella points out, AR’s ability to bring concepts to life through interactive experiences has profound implications for education, making learning more engaging and impactful.
4. Healthcare and medicine
In healthcare, AR is being used to assist with both diagnosis and treatment. Surgeons, for instance, can use AR glasses to overlay critical patient information during surgeries, making procedures more precise and less invasive. This has the potential to reduce complications and enhance patient outcomes. Additionally, AR is being applied in rehabilitation, where patients perform exercises in an environment augmented with helpful visuals or guidance.
Dr. Eric Topol, a cardiologist and digital medicine expert, states, “The potential of augmented reality in healthcare is immense. By providing surgeons with real-time data, we can improve outcomes and revolutionize patient care.” Dr. Topol’s insights highlight how AR can enhance the accuracy of medical procedures and help healthcare professionals make better-informed decisions during treatments.
5. Real Estate and architecture

AR is transforming the real estate and architecture industries by allowing potential buyers to visualize buildings and interiors in 3D before construction begins. With AR, clients can walk through virtual representations of homes or offices, making decisions about layouts, furniture, and finishes. Architects and construction teams can also use AR to visualize how buildings will interact with their surroundings, ensuring that designs are not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing.
Bjarke Ingels, founder of the architectural firm BIG, explains, “Augmented reality has the potential to change the way we design and experience spaces. It provides a new dimension to the planning process and enables better collaboration between designers, builders, and clients.” Ingels’ statement emphasizes how AR can revolutionize architectural design, allowing for greater creativity and precision in planning and execution.
6. Marketing and advertising
Marketing and advertising are among the most rapidly adopting sectors of AR. Brands are using AR to create interactive campaigns that engage consumers in exciting and memorable ways. For instance, AR billboards or advertisements allow users to interact with the ad, offering discounts or special promotions when scanned with a smartphone. Major brands like Pepsi and Coca-Cola have used AR to create captivating interactive experiences, such as virtual product trials or gamified campaigns.
David Droga, founder of the advertising agency Droga5, believes that AR has the power to reshape marketing strategies: “AR in marketing isn’t just a novelty; it’s a powerful tool that can turn passive audiences into active participants. It creates memorable experiences that drive deeper brand engagement.” Droga’s perspective highlights the potential of AR to transform marketing from a traditional, one-way communication model to a dynamic, interactive experience that actively engages customers.
Also read: When was augmented reality created?
Also read: What is one characteristic of augmented reality?
Augmented reality has the potential to change the way we design and experience spaces. It provides a new dimension to the planning process and enables better collaboration between designers, builders, and clients.
Bjarke Ingels, founder of the architectural firm BIG
Benefits of Augmented Reality

The potential benefits of AR are vast, impacting not only industries but also improving daily life for individuals.
1. Enhanced user experience
AR creates richer, more immersive user experiences by blending the digital and physical worlds. Whether it’s seeing how a piece of furniture fits in your home or getting step-by-step instructions on a complicated DIY project, AR makes it easier and more enjoyable to interact with technology.
2. Increased efficiency
In industries like manufacturing and logistics, AR is being used to increase productivity and efficiency. Workers can access real-time data and instructions via AR glasses or devices, allowing them to complete tasks faster and with greater accuracy. In retail, AR helps consumers make quicker decisions by visualizing products in their real-world environment.
3. Better decision-making
AR provides users with more detailed and accurate information about their surroundings. In fields like real estate, healthcare, and education, AR offers the tools to make more informed decisions. Whether it’s visualizing a home design, understanding medical procedures, or exploring historical events, AR helps people make better choices.
4. Immersive learning and training
AR’s ability to create interactive and engaging learning environments is one of its standout features. Students and professionals alike benefit from AR’s capacity to simulate real-world scenarios, which can lead to better knowledge retention and skills development.
Challenges and limitations of Augmented Reality

While augmented reality (AR) holds significant promise, it also faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed before the technology can become fully mainstream and ubiquitous. From hardware constraints to privacy concerns, AR still has obstacles to overcome before it can realize its full potential. Below, we explore some of the key challenges that AR technology is currently grappling with.
1. Hardware limitations
One of the major hurdles facing AR adoption is the current limitations in hardware. Most AR experiences rely on smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses, all of which come with their own set of limitations. Smartphones, while widely accessible, often struggle with battery life, processing power, and screen quality when delivering complex AR experiences. AR glasses, although specialized for immersive experiences, are still bulky, expensive, and not yet suitable for everyday use by the average consumer.
As Tony Fadell, creator of the iPod and founder of Nest Labs, points out, “The hardware for AR is still in its infancy. Until devices are lightweight, affordable, and capable of running complex AR applications without draining battery life, AR will remain a niche technology.” This comment highlights the critical need for technological advancements in AR hardware. Fadell emphasizes that the weight, cost, and performance of AR devices are key barriers to mass adoption. While the potential of AR is immense, hardware innovation must catch up with software to create seamless and efficient experiences for users.
2. Privacy and data security concerns
AR systems often rely on real-time data collection from the user’s environment, which raises significant privacy concerns. For instance, AR glasses and apps that capture real-world visuals can unintentionally record sensitive information without the user’s knowledge. The continuous collection of data such as location, personal preferences, and even conversations poses a serious privacy risk if not managed responsibly.
As Sheryl Sandberg, former COO of Facebook, warns, “As AR technology becomes more pervasive, privacy will be one of its most pressing challenges. It’s crucial that we develop safeguards to ensure that users’ data is protected and that their experiences remain secure.” Sandberg’s statement underscores the urgent need to implement robust privacy frameworks as AR becomes more integrated into everyday life. With the increasing ability of AR systems to collect and process personal data, companies must prioritize security to ensure users feel confident in using the technology. Without appropriate safeguards, privacy concerns could hinder AR’s broader adoption.

3. Social acceptance and user comfort
While AR technology can provide immersive experiences, not everyone is comfortable with the idea of using it in their daily lives. For example, wearing AR glasses or engaging with AR environments can cause discomfort for some users. Issues like eye strain, headaches, and motion sickness are common, especially with long-term use. Additionally, there is a social element to consider—people may feel self-conscious about wearing AR glasses in public or using AR features in spaces where they seem out of place.
Marissa Mayer, former CEO of Yahoo!, highlights the importance of overcoming these barriers: “User comfort and social acceptance are significant barriers to the widespread adoption of AR. For the technology to truly take off, we need to ensure that it’s seamless, natural, and doesn’t impose any discomfort.” Mayer’s insight emphasizes that, beyond the technical challenges, user experience is a critical factor for AR’s future success. The technology must be intuitive, unobtrusive, and comfortable to use for extended periods, and it must fit naturally into users’ social contexts to avoid discomfort or stigma. Addressing these concerns is essential for AR to gain mainstream acceptance.
4. Content and developer ecosystem
Another challenge is the limited content and developer ecosystem available for AR. While the potential for AR is vast, much of the content available today is still experimental, and many developers are hesitant to invest heavily in AR without assurance of its long-term viability. In order for AR to truly reach its potential, there needs to be a larger and more diverse ecosystem of AR apps, games, and practical applications that appeal to a wide variety of users and industries.
John Riccitiello, CEO of Unity Technologies, aptly notes, “Developing compelling AR content is essential for the technology’s growth. Without a strong developer ecosystem and meaningful applications, AR will struggle to reach its potential.” Riccitiello’s comment emphasizes that content is key to AR’s widespread adoption. A thriving developer community and a broad range of practical and engaging AR experiences will be essential for encouraging users to embrace the technology. Until there is more substantive content available, AR’s growth will remain somewhat limited.
Marissa Mayer, former CEO of Yahoo!
The future of Augmented Reality
The future of augmented reality looks promising, with advances in hardware, software, and content creation set to drive the technology forward.
1. Improved hardware
As AR technology evolves, we can expect more affordable, lightweight, and powerful AR glasses and headsets that offer hands-free, immersive experiences. Companies like Microsoft (with its HoloLens) and Magic Leap are already pushing the boundaries of AR hardware, and consumer versions are likely to become more common in the coming years.
2. 5G and AR
The rollout of 5G networks will be a game-changer for augmented reality. With 5G’s ultra-fast speeds and low latency, AR applications will be able to deliver even more immersive experiences with less lag and higher quality. This could allow for real-time AR experiences that were previously not possible due to bandwidth limitations.
3. AI and AR integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to enhance AR experiences even further. AI-powered AR can personalize the experience, recognize objects more accurately, and even predict user behaviors. For example, an AR system could automatically adjust content based on the user’s preferences or environment.
4. AR in everyday life
In the future, AR could become a part of daily life. From navigating cities with AR maps to using AR glasses for hands-free communication, the integration of augmented reality into our everyday routines could revolutionize how we interact with the world around us.
FAQ
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information, such as images, sounds, or other data, onto the real world. Unlike virtual reality, which creates a completely immersive environment, AR enhances your existing environment with virtual elements that interact in real-time with the physical world.
AR works by using a combination of sensors, cameras, and software to capture the user’s environment. The system processes the data, and then overlays digital content onto that environment. This is typically displayed on devices such as smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses, where the virtual objects seem to coexist with the real world, providing an interactive experience.
Augmented Reality (AR) has numerous applications across different industries, transforming the way we interact with the world. In retail, AR enhances shopping experiences with features like virtual try-ons, allowing customers to see how products will look before purchase. In healthcare, AR is used for assisting in surgeries by overlaying crucial information or visualizing medical data, offering real-time support to doctors. The gaming industry benefits from AR through interactive experiences such as Pokémon Go, where virtual characters blend seamlessly with real-world locations, creating an immersive environment. Education also leverages AR by providing interactive learning opportunities, such as visualizing 3D models of historical events or scientific processes, making complex subjects more engaging and easier to understand. Additionally, navigation apps use AR to provide real-time directions, overlaying helpful information when users point their phones at streets, buildings, or landmarks, making navigation more intuitive and user-friendly.
Some key challenges of Augmented Reality (AR) include hardware limitations, privacy and security concerns, user comfort, and content creation. Many AR applications require powerful processing capabilities, which current devices may not fully support, leading to performance issues. Additionally, AR systems often need to collect real-world data, raising concerns about the security and privacy of user information. Extended use of AR devices, such as glasses, can also cause physical discomfort, including eye strain or headaches, limiting their practicality for long periods. Furthermore, there is still a limited amount of high-quality, practical content available for AR applications, which can hinder widespread adoption and make it difficult for users to fully experience the technology’s potential. These challenges must be addressed for AR to reach its full potential and become more integrated into everyday life.
AR is expected to revolutionize various industries by creating more immersive, interactive, and efficient experiences. In the future, AR could transform how we shop, learn, interact with technology, and work. As AR technology continues to evolve and hardware becomes more accessible, it will likely be integrated into everyday life, improving productivity, enhancing entertainment, and changing the way we experience the world around us.

