- IANA is an organisation responsible for the assignment of numbering systems and unique names that form the backbone of the global internet.
- IANA is responsible for the internet address allocation of resources to the various regional organisations.
OUR TAKE
IANA assigns internet numbers to network resources such as IP addresses, domain names, port numbers, and protocol numbers. IANA also maintains and updates various network protocols such as TCP/IP, HTTP, and to ensure the continued availability and compatibility of these protocols. These efforts are all aimed at ensuring the smooth functioning of the global internet and the smooth flow of communications.
–Zora Lin, BTW reporter
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) plays a major role in today’s internet. However, not many know about this organisation or its responsibilities. IANA is a crucial component of the internet’s infrastructure, responsible for the global coordination of the Domain Name System (DNS) Root, IP addressing, and internet protocol parameter assignments.
What is IANA
IANA, or the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, is an organisation responsible for the assignment of numbering systems and unique names that form the backbone of the global internet. Even though the internet is not centralised, we need to manage some of its key elements centrally to achieve global coordination. IANA functions as the administrator that handles this critical coordination. It is one of the several authorities that enable the World Wide Web to be what it is today.
Also read: The internet protocol: A foundational pillar of networking
Also read: Internet Architecture Board (IAB): What is it and how does it work?
Connection between IANA and ICANN
IANA is actually a division of ICANN. This non-profit organisation is made up of a number of organisations representing different databases.
The U.S. Department of Commerce has entrusted ICANN to manage IANA since 1998. However, as of 2016, ICANN merged with Public Technology Identifiers, an affiliate from California, to take over the management of IANA. This marks a historic shift from government regulation to a private sector-led model, reinforcing a multi-stakeholder approach to internet governance.

The company was set up after its contract with the Ministry of Commerce expired. This event is very important because it effectively makes IANA part of the private sector.
Since 2018, IANA has been managed by Kim Davies. Jon Postel and Joyce K. Reynolds ran the business until 1998. Before Davis took over in 2018, three other people ran the organisation, each for several years.
The transition of IANA’s stewardship to the global internet community was a result of a proposal developed by a diverse group of stakeholders, including private-sector representatives, technical experts, academics, civil society, governments, and individual internet users. This transition was seen as a validation of the multistakeholder model of internet governance, ensuring that the internet remains free, open, and accessible.
In the multi-stakeholder model, whether it is governments, private institutions, civil society, other internet organisations, or ordinary internet users, each party is equal, and no party is more important.
Voshia, ICANN’s Stakeholder Engagement Program Leader
History of IANA
The need to manage IP addresses, internet protocols and the DNS was apparent from the early days of the internet. In the beginning, a single person handled the tasks that now require an entire organisation such as IANA. His name was Jon Postel.
In the early 1970s, while working at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), Postel was instrumental in employing the ARPANET protocols and, essentially, building the predecessor of today’s internet. Postel quickly figured out that administering and managing socket numbers was important.
A socket number is a combination of an IP address and a port number. A socket number effectively addresses specific applications on specific computers.
Even though it was easy to manage ARPANET in the early 70s, Postel realised that we shouldn’t use the same numbers for different applications.
There is no organisation in the world that puts everything on the table like ICANN. Any aspect of ICANN’s changes can be discussed.
Fadi Chehadé, Former CEO of ICANN
Postel was known as the Czar of Socket Numbers at the Information Sciences Institute (ISI) at the University of Southern California when he became responsible for handling them. However, officially, DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) handled this responsibility.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority came into the picture in 1988. Until 1998, both DARPA and ISI funded it.
NTIA (National Telecommunications and Information Administration) at the United States Department of Commerce released the Management of internet Names and Addresses white paper in 1998. This is when ICANN, a private organisation, became responsible for IANA.
The US government continued supervising the authority until 2016. Afterward, IANA’s responsibilities moved entirely to the private sector.
Pop quiz:
In which year was IANA taken over by ICANN?
A. 2014
B. 2015
C. 2016
D. 2017
The correct answer is at the bottom of the article.
Three main types of internet identifiers managed by IANA
The primary function of IANA is to make sure these essential values and names remain unique and publicly available. To understand what all of this means exactly, let’s take a look at each of the three responsibilities and what IANA actually does.
DNS root zone
The DNS is a hierarchical database that connects domain names to an IP address. This further enables computers to send data to each other.
IANA is responsible for domain name management of DNS root servers and the DNS root itself. In simpler terms, IANA manages the DNS root zone that keeps the data at the top-level domains like .com and .net.
IANA also administers the central collection of all allowed internationalised domain names. They are commonly known as special character domains.
IP addresses
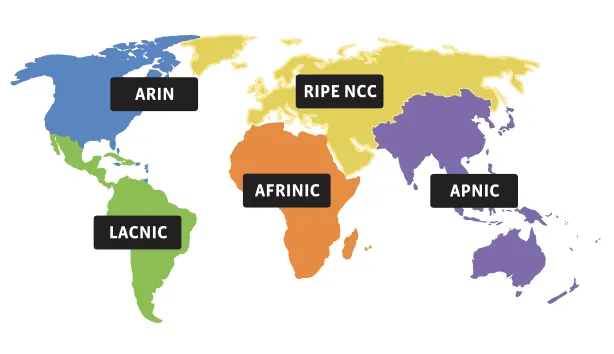
IANA manages the global pool of IP addresses (both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses). It also manages AS numbers (ASNs) that are assigned to five Regional Internet Registries (RIRs). Here are each RIR handles a specific part of the globe:
AFRINIC – Africa
APNIC – East Asia, Australia and Oceania
ARIN – USA, Canada and some Caribbean islands
LACNIC – South America, Mexico and some Caribbean islands
RIPE NCC – Europe, Middle East and Central Asia
IANA assigns blocks of IP addresses to each Regional Internet Registry. Subsequently, RIRs split the blocks into smaller blocks and assign them to respective National Internet Registries (NIRs) and Local Internet Registries (LIRs). Finally, these registries pass the blocks of IP addresses to different internet service providers that handle your internet connection.
IANA reserves these blocks of private IP addresses for network administrators:
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 – 72.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
The internet is open. From the beginning of its establishment to the present, the rapid development of the internet depends on the active construction and participation of enterprises, users, governments, non-governmental organisations and other parties. So internet governance should allow all stakeholders to participate and express their demands.
Fadi Chehadé, Former CEO of ICANN
Protocol parameters
For the internet to work, a mutual understanding between computers is necessary. That’s where protocol parameters, or specific numbers used in networking protocols, come into the picture. For computers to understand each other, these protocol parameters need to be unique. Thus, IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) introduced technical protocol standards.
IANA’s task here is to maintain and publish the protocol registries so that software makers can enable seamless communication. Here are some of the common parameters are: HTTP status codes, Port numbers, Language abbreviations.
HTTP status codes inform a user if a request to a server has been processed successfully, if authentication is needed or if an error occurred. For instance, the dreaded 404 (Not Found) error that all internet users know is an HTTP status code, but there are many other HTTP status codes.
Port numbers help identify the senders and recipients of data packets. There are 65,535 ports per IP address, and they all fall into different categories. Each port is reserved for a particular task. For example, port 80 is used for surfing the web.
IANA handles ports up to port 49,151, while the remaining ones are dynamic and not connected to a specific application. Language abbreviations show the language of specific content. EN determines English, ES determines Spanish, FR determines French and so on.
In ICANN, government participation is insufficient, voice channels are few, and means to safeguard public interests are limited. Therefore, it is hoped that ICANN will reform its structure and enhance the role and function of the government.
Representative of the Chinese government
Contributions of IANA
1. Internet addresses the allocation of resources: IANA is responsible for the internet address allocation of resources to the various regional organisations. These regional groups in turn distribute addresses to internet service providers (ISPs), ensuring the functioning and expansion of the internet.
2. Internet protocol registries: As the central registry of the IETF project, IANA is responsible for many internet protocol registries, in particular for TCP port numbers and MIME types. These registration requirements are fundamental to the development of internet technologies and applications, and IANA’s registration efforts are critical to maintaining the uniformity and compatibility of internet standards.
3. Technical contributions: Although IANA is mainly concerned with the technical management and standard setting of the internet, its work has played an important role in promoting the development and application of internet technology. By managing and allocating internet address resources, and registering internet protocols, IANA provides a stable and efficient network service for internet users around the world.
In summary, IANA has made important contributions to the development and application of the internet worldwide through its work in managing and allocating internet address resources, , and as the core registry of IETF projects.
The correct answer is C, 2016.

